Pan-European Study on the Prevalence of the Feline Leukaemia Virus Infection - Reported by the European Advisory Board on Cat Diseases (ABCD Europe)
- PMID: 31671816
- PMCID: PMC6893802
- DOI: 10.3390/v11110993
Pan-European Study on the Prevalence of the Feline Leukaemia Virus Infection - Reported by the European Advisory Board on Cat Diseases (ABCD Europe)
Abstract
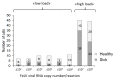
Feline leukaemia virus (FeLV) is a retrovirus associated with fatal disease in progressively infected cats. While testing/removal and vaccination led to a decreased prevalence of FeLV, recently, this decrease has reportedly stagnated in some countries. This study aimed to prospectively determine the prevalence of FeLV viraemia in cats taken to veterinary facilities in 32 European countries. FeLV viral RNA was semiquantitatively detected in saliva, using RT-qPCR as a measure of viraemia. Risk and protective factors were assessed using an online questionnaire to report geographic, demographic, husbandry, FeLV vaccination, and clinical data. The overall prevalence of FeLV viraemia in cats visiting a veterinary facility, of which 10.4% were shelter and rescue cats, was 2.3% (141/6005; 95% CI: 2.0%-2.8%) with the highest prevalences in Portugal, Hungary, and Italy/Malta (5.7%-8.8%). Using multivariate analysis, seven risk factors (Southern Europe, male intact, 1-6 years of age, indoor and outdoor or outdoor-only living, living in a group of ≥5 cats, illness), and three protective factors (Northern Europe, Western Europe, pedigree cats) were identified. Using classification and regression tree (CART) analysis, the origin of cats in Europe, pedigree, and access to outdoors were important predictors of FeLV status. FeLV-infected sick cats shed more viral RNA than FeLV-infected healthy cats, and they suffered more frequently from anaemia, anorexia, and gingivitis/stomatitis than uninfected sick cats. Most cats had never been FeLV-vaccinated; vaccination rates were indirectly associated with the gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. In conclusion, we identified countries where FeLV was undetectable, demonstrating that the infection can be eradicated and highlighting those regions where awareness and prevention should be increased.
Keywords: FeLV; RT-qPCR; gross domestic product at purchasing power parity per capita; prevalence; protective factors; retrovirus; risk factors; vaccination; veterinary sciences; virus shedding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The funders had no influence on the study design, execution and the data analysis. The final manuscript has been accepted by the funders.
Figures
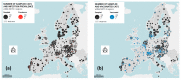
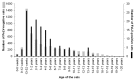

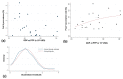
References
-
- Helfer-Hungerbuehler A.K., Widmer S., Kessler Y., Riond B., Boretti F.S., Grest P., Lutz H., Hofmann-Lehmann R. Long-term follow up of feline leukemia virus infection and characterization of viral RNA loads using molecular methods in tissues of cats with different infection outcomes. Virus Res. 2015;197:137–150. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.12.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hofmann-Lehmann R., Holznagel E., Ossent P., Lutz H. Parameters of disease progression in long-term experimental feline retrovirus (feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukemia virus) infections: Hematology, clinical chemistry, and lymphocyte subsets. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1997;4:33–42. - PMC - PubMed

