Structural organization of the C1a-e-c supercomplex within the ciliary central apparatus
- PMID: 31672705
- PMCID: PMC6891083
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201906006
Structural organization of the C1a-e-c supercomplex within the ciliary central apparatus
Abstract
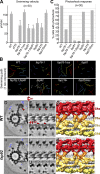
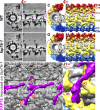
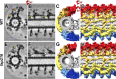
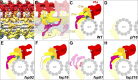
Nearly all motile cilia contain a central apparatus (CA) composed of two connected singlet microtubules with attached projections that play crucial roles in regulating ciliary motility. Defects in CA assembly usually result in motility-impaired or paralyzed cilia, which in humans causes disease. Despite their importance, the protein composition and functions of the CA projections are largely unknown. Here, we integrated biochemical and genetic approaches with cryo-electron tomography to compare the CA of wild-type Chlamydomonas with CA mutants. We identified a large (>2 MD) complex, the C1a-e-c supercomplex, that requires the PF16 protein for assembly and contains the CA components FAP76, FAP81, FAP92, and FAP216. We localized these subunits within the supercomplex using nanogold labeling and show that loss of any one of them results in impaired ciliary motility. These data provide insight into the subunit organization and 3D structure of the CA, which is a prerequisite for understanding the molecular mechanisms by which the CA regulates ciliary beating.
© 2019 Fu et al.
Figures




References
-
- Bower R., VanderWaal K., O’Toole E., Fox L., Perrone C., Mueller J., Wirschell M., Kamiya R., Sale W.S., and Porter M.E.. 2009. IC138 defines a subdomain at the base of the I1 dynein that regulates microtubule sliding and flagellar motility. Mol. Biol. Cell. 20:3055–3063. 10.1091/mbc.e09-04-0277 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

