NK cell defects in X-linked pigmentary reticulate disorder
- PMID: 31672938
- PMCID: PMC6948767
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.125688
NK cell defects in X-linked pigmentary reticulate disorder
Abstract
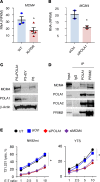
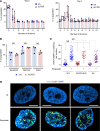
X-linked reticulate pigmentary disorder (XLPDR, Mendelian Inheritance in Man #301220) is a rare syndrome characterized by recurrent infections and sterile multiorgan inflammation. The syndrome is caused by an intronic mutation in POLA1, the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase-α (Pol-α), which is responsible for Okazaki fragment synthesis during DNA replication. Reduced POLA1 expression in this condition triggers spontaneous type I interferon expression, which can be linked to the autoinflammatory manifestations of the disease. However, the history of recurrent infections in this syndrome is as yet unexplained. Here we report that patients with XLPDR have reduced NK cell cytotoxic activity and decreased numbers of NK cells, particularly differentiated, stage V, cells (CD3-CD56dim). This phenotype is reminiscent of hypomorphic mutations in MCM4, which encodes a component of the minichromosome maintenance (MCM) helicase complex that is functionally linked to Pol-α during the DNA replication process. We find that POLA1 deficiency leads to MCM4 depletion and that both can impair NK cell natural cytotoxicity and show that this is due to a defect in lytic granule polarization. Altogether, our study provides mechanistic connections between Pol-α and the MCM complex and demonstrates their relevance in NK cell function.
Keywords: Infectious disease; Inflammation; Innate immunity; Monogenic diseases; NK cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Immune Dysfunction in Mendelian Disorders of POLA1 Deficiency.J Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb;41(2):285-293. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00953-w. Epub 2021 Jan 3. J Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33392852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filaggrin-Associated Atopic Skin, Eye, Airways, and Gut Disease, Modifying the Presentation of X-Linked Reticular Pigmentary Disorder (XLPDR).J Clin Immunol. 2024 Jan 2;44(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01637-x. J Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38165470
-
Image Gallery: Cutaneous findings in an adult with X-linked reticulate pigmentary disorder.Br J Dermatol. 2019 Feb;180(2):e37. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17327. Br J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30714101 No abstract available.
-
DNA polymerase-α regulates the activation of type I interferons through cytosolic RNA:DNA synthesis.Nat Immunol. 2016 May;17(5):495-504. doi: 10.1038/ni.3409. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Nat Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27019227 Free PMC article.
-
Does Natural Killer Cell Deficiency (NKD) Increase the Risk of Cancer? NKD May Increase the Risk of Some Virus Induced Cancer.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 19;10:1703. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01703. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31379882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unwinding the Role of the CMG Helicase in Inborn Errors of Immunity.J Clin Immunol. 2023 Jul;43(5):847-861. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01437-3. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36809597 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Dysfunction in Mendelian Disorders of POLA1 Deficiency.J Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb;41(2):285-293. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00953-w. Epub 2021 Jan 3. J Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33392852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of DNA Polymerase Genes in Amazonian Amerindian Populations.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 24;14(1):53. doi: 10.3390/genes14010053. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36672794 Free PMC article.
-
Variable Syndromic Immunodeficiency in Patients with Biallelic PRIM1 Mutations.J Clin Immunol. 2024 May 22;44(6):129. doi: 10.1007/s10875-024-01733-6. J Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38773012 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular diagnosis of childhood immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, and enteropathy, and implications for clinical management.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Jan;149(1):327-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.04.005. Epub 2021 Apr 20. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 33864888 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

