Theabrownin from Pu-erh tea attenuates hypercholesterolemia via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism
- PMID: 31672964
- PMCID: PMC6823360
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12896-x
Theabrownin from Pu-erh tea attenuates hypercholesterolemia via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism
Abstract
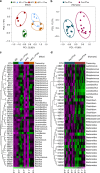
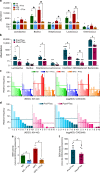
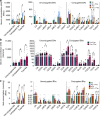
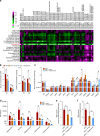
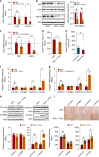
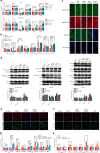
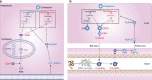
Pu-erh tea displays cholesterol-lowering properties, but the underlying mechanism has not been elucidated. Theabrownin is one of the most active and abundant pigments in Pu-erh tea. Here, we show that theabrownin alters the gut microbiota in mice and humans, predominantly suppressing microbes associated with bile-salt hydrolase (BSH) activity. Theabrownin increases the levels of ileal conjugated bile acids (BAs) which, in turn, inhibit the intestinal FXR-FGF15 signaling pathway, resulting in increased hepatic production and fecal excretion of BAs, reduced hepatic cholesterol, and decreased lipogenesis. The inhibition of intestinal FXR-FGF15 signaling is accompanied by increased gene expression of enzymes in the alternative BA synthetic pathway, production of hepatic chenodeoxycholic acid, activation of hepatic FXR, and hepatic lipolysis. Our results shed light into the mechanisms behind the cholesterol- and lipid-lowering effects of Pu-erh tea, and suggest that decreased intestinal BSH microbes and/or decreased FXR-FGF15 signaling may be potential anti-hypercholesterolemia and anti-hyperlipidemia therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cao ZH, et al. Effect of pu-erh tea on body fat and lipid profiles in rats with diet-induced obesity. Phytother. Res. 2011;25:234–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

