The 14q32 maternally imprinted locus is a major source of longitudinally stable circulating microRNAs as measured by small RNA sequencing
- PMID: 31673048
- PMCID: PMC6823392
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-51948-6
The 14q32 maternally imprinted locus is a major source of longitudinally stable circulating microRNAs as measured by small RNA sequencing
Abstract
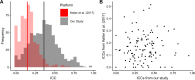
Understanding the normal temporal variation of serum molecules is a critical factor for identifying useful candidate biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of chronic disease. Using small RNA sequencing in a longitudinal study of 66 women with no history of cancer, we determined the distribution and dynamics (via intraclass correlation coefficients, ICCs) of the miRNA profile over 3 time points sampled across 2-5 years in the course of the screening trial, UKCTOCS. We were able to define a subset of longitudinally stable miRNAs (ICC >0.75) that were individually discriminating of women who had no cancer over the study period. These miRNAs were dominated by those originating from the C14MC cluster that is subject to maternal imprinting. This assessment was not significantly affected by common confounders such as age, BMI or time to centrifugation nor alternative methods to data normalisation. Our analysis provides important benchmark data supporting the development of miRNA biomarkers for the impact of life-course exposure as well as diagnosis and prognostication of chronic disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
An imprinted non-coding genomic cluster at 14q32 defines clinically relevant molecular subtypes in osteosarcoma across multiple independent datasets.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 May 15;10(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0465-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28506242 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinted DLK1-DIO3 region of 14q32 defines a schizophrenia-associated miRNA signature in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Mol Psychiatry. 2012 Jul;17(8):827-40. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.78. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 21727898 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of a large microRNA cluster on human chromosome 14q32 in melanoma: biological effects of mir-376a and mir-376c on insulin growth factor 1 receptor.Mol Cancer. 2012 Jul 2;11:44. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-44. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22747855 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs in cancer: Hope or hype?Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 10;381(1):113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27471105 Review.
-
Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer. 2016 Jun 24;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0536-0. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27343009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Physiological MicroRNA Landscape in Nipple Aspirate Fluid: Differences and Similarities with Breast Tissue, Breast Milk, Plasma and Serum.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 11;21(22):8466. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228466. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33187146 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miRNA Biomarker Signatures in Parkinsonian Syndromes.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10118-10132. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04890-w. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40184025 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-based screening in TARDBP/TDP-43 knock-in motor neurons identifies the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 5;15(1):28555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12147-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40764342 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of differentially expressed brain-enriched microRNAs in the plasma of PD patients.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020 Sep;7(9):1594-1607. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51146. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32860338 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Role of the 14q32 Encoded miRNAs in Endocrine Tumors.Genes (Basel). 2021 May 8;12(5):698. doi: 10.3390/genes12050698. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

