Role of Complement Activation in Allograft Inflammation
- PMID: 31673484
- PMCID: PMC6822566
- DOI: 10.1007/s40472-019-0224-2
Role of Complement Activation in Allograft Inflammation
Abstract
Purpose: Novel paradigms have broadened our understanding of mechanisms through which complement mediates allograft inflammation/injury. Herein we review advances in the field and highlight therapeutic implications.
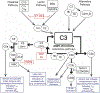
Recent findings: Pre-clinical and translational human trials have elucidated complement-dependent mechanisms of post-transplant ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. Immune cell-derived, and intracellular, complement activation are newly linked to proinflammatory T cell immunity relevant to allograft rejection. Complement-induced immune regulation, including C5a ligation of C5a receptor 2 on T cells, C5a/C5a receptor 1 interactions on regulatory myeloid cells, and C1q binding to CD8+ T cells can inhibit proinflammatory T cells and/or prolong murine allograft survival. Pilot trials of complement inhibition to treat/prevent human I/R- or antibody-initiated allograft injury show promise.
Summary: The complement system participates in allograft injury through multiple context- dependent mechanisms involving various components and receptors. These new insights along with development and implementation of individualized complement inhibitory strategies have potential to improve transplant outcomes.
Keywords: Allograft Inflammation; Antibody Mediated Rejection; Complement; Ischemia Reperfusion Injury; T cell Activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose
Figures
References
-
-
Cravedi P, Leventhal J, Lakhani P, Ward SC, Donovan MJ, Heeger PS. Immune cell-derived C3a and C5a costimulate human T cell alloimmunity. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(10):2530–9.
Study showing complement regulation of T cell immunity is operant in human cells.
-
-
- Arnold JN, Dwek RA, Rudd PM, Sim RB. Mannan binding lectin and its interaction with immunoglobulins in health and in disease. Immunol Lett. 2006;106(2):103–10. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Takahashi K, Alicot EM, Vorup-Jensen T, Kessler B, Thiel S, et al. Activation of the lectin pathway by natural IgM in a model of ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Immunol. 2006;177(7):4727–34. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
