The Effect of a Complex Intervention Program for Unilateral Neglect in Patients with Acute-Phase Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31673487
- PMCID: PMC6816354
- DOI: 10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.5.02
The Effect of a Complex Intervention Program for Unilateral Neglect in Patients with Acute-Phase Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to examine the combined effects of Prism Adaptation (PA) plus functional electrical stimulation (FES) on stroke patients with unilateral neglect, and suggest a new intervention method for acute-phase stroke patients.
Methods: There were 30 patients included in this study from April to October 2016 that had unilateral neglect whilst hospitalized following a stroke (diagnosed by a professional). The participants, who were patients receiving occupational therapy, understood the purpose of the study and agreed to participate. The patients were randomly divided into 3 groups: PA plus FES group (Group A), PA group (Group B), and FES group (Group C). Treatments lasted for 50 minutes per day, 5 times per week, for 3 weeks in total. Reevaluation was conducted after 3 weeks of intervention.
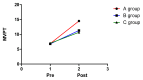
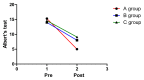
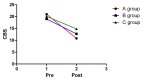
Results: All 3 groups showed unilateral neglect reduction after the intervention, but PA plus FES (complex intervention method) was more effective than PA or FES alone [effect size: Motor-free Visual Perception Test (0.80), Albert test (0.98), CBS (0.92)].
Conclusion: The results of this study support further studies to examine complex intervention for the treatment of unilateral neglect.
Keywords: electrical stimulation; prism adaptation; stroke.
Copyright ©2019, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Trombly CA, Radomski MV. Occupational therapy for physical dysfunction. 7th edition. Baltimore (BA): Lippincott; 2013. pp. 672–4.
-
- Kim SH, Kim TW. Changing degree of activity of daily living performance ability after early occupational therapy intervention for stroke patient. J Occup Ther Aged Dement. 2008;2(1):21–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

