An Integrated Framework for Reducing Hospital Readmissions using Risk Trajectories Characterization and Discharge Timing Optimization
- PMID: 31673670
- PMCID: PMC6822616
- DOI: 10.1080/24725579.2019.1584133
An Integrated Framework for Reducing Hospital Readmissions using Risk Trajectories Characterization and Discharge Timing Optimization
Abstract
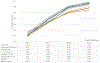
When patients leave the hospital for lower levels of care, they experience a risk of adverse events on a daily basis. The advent of value-based purchasing among other major initiatives has led to an increasing emphasis on reducing the occurrences of these post-discharge adverse events. This has spurred the development of new prediction technologies to identify which patients are at risk for an adverse event as well as actions to mitigate those risks. Those actions include pre-discharge and post-discharge interventions to reduce risk. However, traditional prediction models have been developed to support only post-discharge actions; predicting risk of adverse events at the time of discharge only. In this paper we develop an integrated framework of risk prediction and discharge optimization that supports both types of interventions: discharge timing and post-discharge monitoring. Our method combines a kernel approach for capturing the non-linear relationship between length of stay and risk of an adverse event, with a Principle Component Analysis method that makes the resulting estimation tractable. We then demonstrate how this prediction model could be used to support both types of interventions by developing a simple and easily implementable discharge timing optimization.
Keywords: Cox Mixture Model; Discharge Decision Optimization; Expectation-Maximization Algorithm; Kernel PCA; Readmission Prediction.
Figures
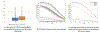
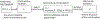
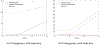
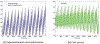
Similar articles
-
Identifying patients at highest-risk: the best timing to apply a readmission predictive model.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019 Jun 26;19(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12911-019-0836-6. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019. PMID: 31242886 Free PMC article.
-
Don't let go of the rope: reducing readmissions by recognizing hospitals' fiduciary duties to their discharged patients.Am Univ Law Rev. 2013;62(3):513-76. Am Univ Law Rev. 2013. PMID: 25335199
-
Readmission Risk Trajectories for Patients With Heart Failure Using a Dynamic Prediction Approach: Retrospective Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2019 Sep 16;7(4):e14756. doi: 10.2196/14756. JMIR Med Inform. 2019. PMID: 31579025 Free PMC article.
-
Readmission risk factors after hospital discharge among the elderly.Popul Health Manag. 2012 Dec;15(6):338-51. doi: 10.1089/pop.2011.0095. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Popul Health Manag. 2012. PMID: 22823255 Review.
-
Discharge Interventions and Modifiable Risk Factors for Preventing Hospital Readmissions in Children with Medical Complexity.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2017;12(4):290-297. doi: 10.2174/1574887112666170816144455. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2017. PMID: 28814257 Review.
Cited by
-
Discharge interventions from inpatient child and adolescent mental health care: a scoping review.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022 Jun;31(6):857-878. doi: 10.1007/s00787-020-01634-0. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 32886222 Free PMC article.
-
A Functional Model for Structure Learning and Parameter Estimation in Continuous Time Bayesian Network: An Application in Identifying Patterns of Multiple Chronic Conditions.IEEE Access. 2021;9:148076-148089. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3122912. Epub 2021 Oct 26. IEEE Access. 2021. PMID: 35371895 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of artificial intelligence to improve patient flow on mental health inpatient units - Narrative literature review.Heliyon. 2021 Apr 15;7(4):e06626. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06626. eCollection 2021 Apr. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33898804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Care Strategies for Reducing Hospital Readmissions Using Stochastic Programming.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Jul 26;9(8):940. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9080940. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34442079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson David, Golden Bruce, Jank Wolfgang, Wasil Edward. 2012. The impact of hospital utilization on patient readmission rate. Health care management science 15(1) 29–36. - PubMed
-
- Anderson David, Price Carter, Golden Bruce, Jank Wolfgang, Wasil Edward. 2011. Examining the discharge practices of surgeons at a large medical center. Health care management science 14(4) 338–347. - PubMed
-
- Ata Bariş, Shneorson Shiri. 2006. Dynamic control of an M/M/1 service system with adjustable arrival and service rates. Management Science 52(11) 1778–1791.
-
- Bartel Ann P, Chan Carri W, Kim Song-Hee Hailey. 2014. Should hospitals keep their patients longer? the role of inpatient care in reducing post-discharge mortality. Tech. rep., National Bureau of Economic Research.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
