Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome: A Rare, Mosaic Disease of Gα s Activation
- PMID: 31673695
- PMCID: PMC7127130
- DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnz011
Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome: A Rare, Mosaic Disease of Gα s Activation
Abstract
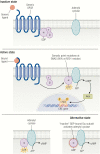
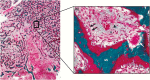
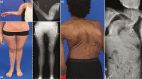
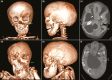
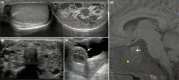
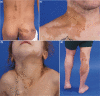
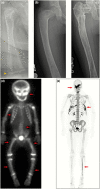
Fibrous dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome (FD/MAS) is a rare disorder of striking complexity. It arises from somatic, gain-of-function mutations in GNAS, leading to mosaic Gα s activation and inappropriate production of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). The clinical phenotype is largely determined by the location and extent of affected tissues, and the pathophysiological effects of Gα s activation within these tissues. In bone, Gα s activation results in impaired differentiation of skeletal stem cells, leading to discrete skeletal lesions prone to fracture, deformity, and pain. Extraskeletal manifestations include a variable combination of hyperpigmented macules and hyperfunctioning endocrinopathies. Distinctive age-related changes in disease development has key effects on histologic, radiographic, and clinical features. FD/MAS thus presents along a uniquely broad clinical spectrum, and the resulting challenges in diagnosis and management can be difficult for clinicians. This review presents FD/MAS in the context of a mosaic disorder of Gα s activation, providing an intellectual framework within which to understand, evaluate, and treat this interesting disease. It includes a comprehensive summary of current understanding of FD/MAS pathogenesis, and a detailed discussion of clinical presentation and management. Critical areas of unmet need are highlighted, including discussion of key challenges and potential solutions to advance research and clinical care in FD/MAS.
Keywords: fibroblast growth factor 23; growth hormone excess; metabolic bone disease; precocious puberty; skeletal stem cells; somatic mosaicism.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society 2019.
Figures

References
-
- Boyce AM, Florenzano P, de Castro LF, Collins MT. Fibrous dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K, Amemiya A, eds. GeneReviews®. Seattle, WA: University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2020. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein LS, Shenker A, Gejman PV, Merino MJ, Friedman E, Spiegel AM. Activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein in the McCune-Albright syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991;325(24):1688–1695. - PubMed
-
- Riminucci M, Fisher LW, Majolagbe A, et al. . A novel GNAS1 mutation, R201G, in McCune-Albright syndrome. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(11):1987–1989. - PubMed
-
- Idowu BD, Al-Adnani M, O’Donnell P, et al. . A sensitive mutation-specific screening technique for GNAS1 mutations in cases of fibrous dysplasia: the first report of a codon 227 mutation in bone. Histopathology. 2007;50(6):691–704. - PubMed

