Retro-2 protects cells from ricin toxicity by inhibiting ASNA1-mediated ER targeting and insertion of tail-anchored proteins
- PMID: 31674906
- PMCID: PMC6858068
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.48434
Retro-2 protects cells from ricin toxicity by inhibiting ASNA1-mediated ER targeting and insertion of tail-anchored proteins
Abstract
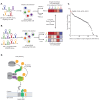
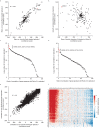
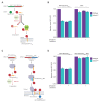
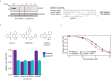
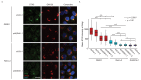
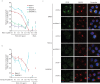
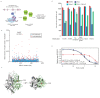
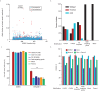
The small molecule Retro-2 prevents ricin toxicity through a poorly-defined mechanism of action (MOA), which involves halting retrograde vesicle transport to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). CRISPRi genetic interaction analysis revealed Retro-2 activity resembles disruption of the transmembrane domain recognition complex (TRC) pathway, which mediates post-translational ER-targeting and insertion of tail-anchored (TA) proteins, including SNAREs required for retrograde transport. Cell-based and in vitro assays show that Retro-2 blocks delivery of newly-synthesized TA-proteins to the ER-targeting factor ASNA1 (TRC40). An ASNA1 point mutant identified using CRISPR-mediated mutagenesis abolishes both the cytoprotective effect of Retro-2 against ricin and its inhibitory effect on ASNA1-mediated ER-targeting. Together, our work explains how Retro-2 prevents retrograde trafficking of toxins by inhibiting TA-protein targeting, describes a general CRISPR strategy for predicting the MOA of small molecules, and paves the way for drugging the TRC pathway to treat broad classes of viruses known to be inhibited by Retro-2.
Keywords: CRISPR; Retro-2; TRC pathway; cell biology; genetics; genomics; human.
© 2019, Morgens et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DM, CC, AK, NW, AL, MD, CT, GH, AL, KH, NP, JZ, EH, PA, AD, DY, RA, JS, VD, MB No competing interests declared
Figures



References
-
- Acosta-Alvear D, Cho MY, Wild T, Buchholz TJ, Lerner AG, Simakova O, Hahn J, Korde N, Landgren O, Maric I, Choudhary C, Walter P, Weissman JS, Kampmann M. Paradoxical resistance of multiple myeloma to proteasome inhibitors by decreased levels of 19S proteasomal subunits. eLife. 2015;4:e08153. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08153. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amessou M, Fradagrada A, Falguières T, Lord JM, Smith DC, Roberts LM, Lamaze C, Johannes L. Syntaxin 16 and syntaxin 5 are required for efficient retrograde transport of several exogenous and endogenous cargo proteins. Journal of Cell Science. 2007;120:1457–1468. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03436. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassik MC, Kampmann M, Lebbink RJ, Wang S, Hein MY, Poser I, Weibezahn J, Horlbeck MA, Chen S, Mann M, Hyman AA, Leproust EM, McManus MT, Weissman JS. A systematic mammalian genetic interaction map reveals pathways underlying ricin susceptibility. Cell. 2013;152:909–922. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carney DW, Nelson CD, Ferris BD, Stevens JP, Lipovsky A, Kazakov T, DiMaio D, Atwood WJ, Sello JK. Structural optimization of a retrograde trafficking inhibitor that protects cells from infections by human polyoma- and papillomaviruses. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2014;22:4836–4847. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.06.053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

