An efficient CRISPR-based strategy to insert small and large fragments of DNA using short homology arms
- PMID: 31674908
- PMCID: PMC6855806
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.51539
An efficient CRISPR-based strategy to insert small and large fragments of DNA using short homology arms
Abstract
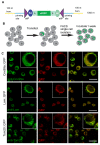
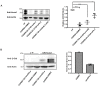
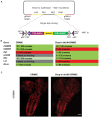
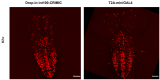
We previously reported a CRISPR-mediated knock-in strategy into introns of Drosophila genes, generating an attP-FRT-SA-T2A-GAL4-polyA-3XP3-EGFP-FRT-attP transgenic library for multiple uses (Lee et al., 2018a). The method relied on double stranded DNA (dsDNA) homology donors with ~1 kb homology arms. Here, we describe three new simpler ways to edit genes in flies. We create single stranded DNA (ssDNA) donors using PCR and add 100 nt of homology on each side of an integration cassette, followed by enzymatic removal of one strand. Using this method, we generated GFP-tagged proteins that mark organelles in S2 cells. We then describe two dsDNA methods using cheap synthesized donors flanked by 100 nt homology arms and gRNA target sites cloned into a plasmid. Upon injection, donor DNA (1 to 5 kb) is released from the plasmid by Cas9. The cassette integrates efficiently and precisely in vivo. The approach is fast, cheap, and scalable.
Keywords: CRIMIC; CRISPR; D. melanogaster; drop-in; drosophila; genetics; genomics; homologous recombination.
© 2019, Kanca et al.
Conflict of interest statement
OK, JZ, JG, SK, DY, GA, HC, ZZ, LM, YH, WL, YF, MG, SY, KS, YH, AS, SM, NP No competing interests declared, HB Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

