The mechanosensitive ion channel TRAAK is localized to the mammalian node of Ranvier
- PMID: 31674909
- PMCID: PMC6824864
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.50403
The mechanosensitive ion channel TRAAK is localized to the mammalian node of Ranvier
Abstract
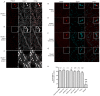
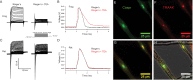
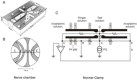
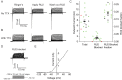
TRAAK is a membrane tension-activated K+ channel that has been associated through behavioral studies to mechanical nociception. We used specific monoclonal antibodies in mice to show that TRAAK is localized exclusively to nodes of Ranvier, the action potential propagating elements of myelinated nerve fibers. Approximately 80 percent of myelinated nerve fibers throughout the central and peripheral nervous system contain TRAAK in what is likely an all-nodes or no-nodes per axon fashion. TRAAK is not observed at the axon initial segment where action potentials are first generated. We used polyclonal antibodies, the TRAAK inhibitor RU2 and node clamp amplifiers to demonstrate the presence and functional properties of TRAAK in rat nerve fibers. TRAAK contributes to the 'leak' K+ current in mammalian nerve fiber conduction by hyperpolarizing the resting membrane potential, thereby increasing Na+ channel availability for action potential propagation. We speculate on why nodes of Ranvier contain a mechanosensitive K+ channel.
Keywords: mechanosensation; mouse; neuroscience; node of Ranvier; node-clamp; rat; xenopus.
© 2019, Brohawn et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SB, WW, AH, EC, JS, RM No competing interests declared
Figures











References
-
- Arroyo EJ. Myelin Biology and Disorders. Academic Press; 2004. - DOI
-
- Bauer CK, Calligari P, Radio FC, Caputo V, Dentici ML, Falah N, High F, Pantaleoni F, Barresi S, Ciolfi A, Pizzi S, Bruselles A, Person R, Richards S, Cho MT, Claps Sepulveda DJ, Pro S, Battini R, Zampino G, Digilio MC, Bocchinfuso G, Dallapiccola B, Stella L, Tartaglia M. Mutations in KCNK4 that affect gating cause a recognizable neurodevelopmental syndrome. The American Journal of Human Genetics. 2018;103:621–630. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.09.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

