Quinoline-Conjugated Ruthenacarboranes: Toward Hybrid Drugs with a Dual Mode of Action
- PMID: 31675152
- PMCID: PMC6973020
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201900349
Quinoline-Conjugated Ruthenacarboranes: Toward Hybrid Drugs with a Dual Mode of Action
Abstract
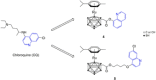
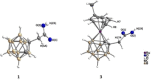
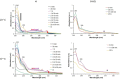
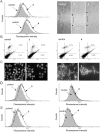
The role of autophagy in cancer is often complex, ranging from tumor-promoting to -suppressing effects. In this study, two novel hybrid molecules were designed, containing a ruthenacarborane fragment conjugated with a known modulator of autophagy, namely a quinoline derivative. The complex closo-[3-(η6 -p-cymene)-1-(quinolin-8-yl-acetate)-3,1,2-RuC2 B9 H10 ] (4) showed a dual mode of action against the LN229 (human glioblastoma) cell line, where it inhibited tumor-promoting autophagy, and strongly inhibited cell proliferation, de facto blocking cellular division. These results, together with the tendency to spontaneously form nanoparticles in aqueous solution, make complex 4 a very promising drug candidate for further studies in vivo, for the treatment of autophagy-prone glioblastomas.
Keywords: autophagy; glioblastoma; quinoline; ruthenacarborane; self-assembly.
©2019 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hey-Hawkins E., Viñas Teixidor C. (Eds.) Boron-Based Compounds, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK, 2018.
-
- None
-
- Stockmann P., Gozzi M., Kuhnert R., Sárosi M. B., Hey-Hawkins E., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3497–3512; - PubMed
-
- Zargham E. O., Mason C. A., M. W. Lee Jr , Int. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 6;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

