Discovery of Human Signaling Systems: Pairing Peptides to G Protein-Coupled Receptors
- PMID: 31675498
- PMCID: PMC6838683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.010
Discovery of Human Signaling Systems: Pairing Peptides to G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Abstract
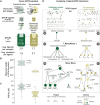
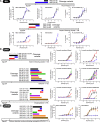
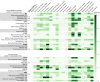
The peptidergic system is the most abundant network of ligand-receptor-mediated signaling in humans. However, the physiological roles remain elusive for numerous peptides and more than 100 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Here we report the pairing of cognate peptides and receptors. Integrating comparative genomics across 313 species and bioinformatics on all protein sequences and structures of human class A GPCRs, we identify universal characteristics that uncover additional potential peptidergic signaling systems. Using three orthogonal biochemical assays, we pair 17 proposed endogenous ligands with five orphan GPCRs that are associated with diseases, including genetic, neoplastic, nervous and reproductive system disorders. We also identify additional peptides for nine receptors with recognized ligands and pathophysiological roles. This integrated computational and multifaceted experimental approach expands the peptide-GPCR network and opens the way for studies to elucidate the roles of these signaling systems in human physiology and disease. VIDEO ABSTRACT.
Keywords: GPCR; deorphanization; endogenous ligand; evolution; genomics; machine learning; orphan receptor; peptide ligand; pharmacological screening; receptor internalization.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
L.M.H.-K. is an employee of PolyPeptide Group, Sweden.
Figures












References
-
- Alhouayek M., Masquelier J., Muccioli G.G. Lysophosphatidylinositols, from Cell Membrane Constituents to GPR55 Ligands. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018;39:586–604. - PubMed
-
- Bercher M., Hanson B., van Staden C., Wu K., Ng G.Y., Lee P.H. Agonists of the orphan human G2A receptor identified from inducible G2A expression and beta-lactamase reporter screen. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2009;7:133–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

