Consequences of chronic diseases and other limitations associated with old age - a scoping review
- PMID: 31675997
- PMCID: PMC6823935
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-019-7762-5
Consequences of chronic diseases and other limitations associated with old age - a scoping review
Abstract
Background: The phenomenon of the increasing number of ageing people in the world is arguably the most significant economic, health and social challenge that we face today. Additionally, one of the major epidemiologic trends of current times is the increase in chronic and degenerative diseases. This paper tries to deliver a more up to date overview of chronic diseases and other limitations associated with old age and provide a more detailed outlook on the research that has gone into this field.
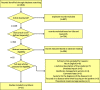
Methods: First, challenges for seniors, including chronic diseases and other limitations associated with old age, are specified. Second, a review of seniors' needs and concerns is performed. Finally, solutions that can improve seniors' quality of life are discussed. Publications obtained from the following databases are used in this scoping review: Web of Science, PubMed, and Science Direct. Four independent reviewers screened the identified records and selected relevant publications published from 2010 to 2017. A total of 1916 publications were selected. In all, 52 papers were selected based on abstract content. For further processing, 21 full papers were screened."
Results: The results indicate disabilities as a major problem associated with seniors' activities of daily living dependence. We founded seven categories of different conditions - psychological problems, difficulties in mobility, poor cognitive function, falls and incidents, wounds and injuries, undernutrition, and communication problems. In order to minimize ageing consequences, some areas require more attention, such as education and training; technological tools; government support and welfare systems; early diagnosis of undernutrition, cognitive impairment, and other diseases; communication solutions; mobility solutions; and social contributions.
Conclusions: This scoping review supports the view on chronic diseases in old age as a complex issue. To prevent the consequences of chronic diseases and other limitations associated with old age related problems demands multicomponent interventions. Early recognition of problems leading to disability and activities of daily living (ADL) dependence should be one of essential components of such interventions.
Keywords: Chronic diseases; Elderly disability, activities of daily living; Seniors’ needs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hill AL, Russell MM. The special needs of elderly patients. Seminars Colon Rectal Surg. 2013;24(4):200–208. doi: 10.1053/j.scrs.2013.08.007. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization . Global health and aging. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- World Health Organization . Towards policy for health and ageing. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

