Neighborhood Poverty and Pediatric Intensive Care Use
- PMID: 31676680
- PMCID: PMC6889973
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2019-0748
Neighborhood Poverty and Pediatric Intensive Care Use
Abstract
Background: Disparities in health service use have been described across a range of sociodemographic factors. Patterns of PICU use have not been thoroughly assessed.
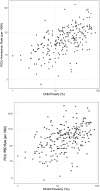
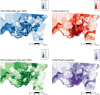
Methods: This was a population-level, retrospective analysis of admissions to the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center PICU between 2011 and 2016. Residential addresses of patients were geocoded and spatially joined to census tracts. Pediatric patients were eligible for inclusion if they resided within Hamilton County, Ohio. PICU admission and bed-day rates were calculated by using numerators of admissions and bed days, respectively, over a denominator of tract child population. Relationships between tract-level PICU use and child poverty were assessed by using Spearman's ρ and analysis of variance. Analyses were event based; children admitted multiple times were counted as discrete admissions.
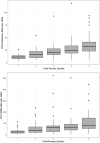
Results: There were 4071 included admissions involving 3129 unique children contributing a total of 12 297 PICU bed days. Child poverty was positively associated with PICU admission rates (r = 0.59; P < .001) and bed-day rates (r = 0.47; P < .001). When tracts were grouped into quintiles based on child poverty rates, the PICU bed-day rate ranged from 23.4 days per 1000 children in the lowest poverty quintile to 81.9 days in the highest poverty quintile (P < .001).
Conclusions: The association between poverty and poor health outcomes includes pediatric intensive care use. This association exists for children who grow up in poverty and around poverty. Future efforts should characterize the interplay between patient- and neighborhood-level risk factors and explore neighborhood-level interventions to improve child health.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Slain KN, Shein SL, Stormorken AG, Broberg MCG, Rotta AT. Outcomes of children with critical bronchiolitis living in poor communities. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2018;57(9):1027–1032 - PubMed
-
- Hakmeh W, Barker J, Szpunar SM, Fox JM, Irvin CB. Effect of race and insurance on outcome of pediatric trauma. Acad Emerg Med. 2010;17(8):809–812 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

