Spatial and temporal axes impact ecology of the gut microbiome in juvenile European lobster (Homarus gammarus)
- PMID: 31676854
- PMCID: PMC6976562
- DOI: 10.1038/s41396-019-0546-1
Spatial and temporal axes impact ecology of the gut microbiome in juvenile European lobster (Homarus gammarus)
Abstract
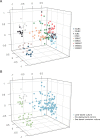
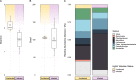
Microbial communities within the gut can markedly impact host health and fitness. To what extent environmental influences affect the differential distribution of these microbial populations may therefore significantly impact the successful farming of the host. Using a sea-based container culture (SBCC) system for the on-growing of European lobster (Homarus gammarus), we tracked the bacterial gut microbiota over a 1-year period. We compared these communities with lobsters of the same cohort, retained in a land-based culture (LBC) system to assess the effects of the culture environment on gut bacterial assemblage and describe the phylogenetic structure of the microbiota to compare deterministic and stochastic assembly across both environments. Bacterial gut communities from SBCCs were generally more phylogenetically clustered, and therefore deterministically assembled, compared to those reared in land-based systems. Lobsters in SBCCs displayed significantly more species-rich and species-diverse gut microbiota compared to those retained in LBC. A reduction in the bacterial diversity of the gut was also associated with higher infection prevalence of the enteric viral pathogen Homarus gammarus nudivirus (HgNV). SBCCs may therefore benefit the overall health of the host by promoting the assembly of a more diverse gut bacterial community and reducing the susceptibility to disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Harris JM. The presence, nature, and role of gut microflora in aquatic invertebrates: a synthesis. Microb Ecol. 1993;25:195–231. - PubMed
-
- Zokaeifar H, Balcázar JL, Saad CR, Kamarudin MS, Sijam K, Arshad A, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, digestive enzymes, immune gene expression and disease resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012;33:683–9. - PubMed
-
- Xiong Jinbo, Dai Wenfang, Zhu Jinyong, Liu Keshao, Dong Chunming, Qiu Qiongfen. The Underlying Ecological Processes of Gut Microbiota Among Cohabitating Retarded, Overgrown and Normal Shrimp. Microbial Ecology. 2016;73(4):988–999. - PubMed
-
- Daniels CL, Merrifield DL, Boothroyd DP, Davies SJ, Factor JR, Arnold KE. Effect of dietary Bacillus spp. and mannan oligosaccharides (MOS) on European lobster (Homarus gammarus L.) larvae growth performance, gut morphology and gut microbiota. Aquaculture. 2010;304:49–57.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- WT097835MF/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/N013891/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT101650MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/K003240/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M008924/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom

