Does ophthalmic-grade silicone oil possess antimicrobial properties?
- PMID: 31677008
- PMCID: PMC6825108
- DOI: 10.1186/s12348-019-0187-6
Does ophthalmic-grade silicone oil possess antimicrobial properties?
Abstract
Purpose: To test the antimicrobial properties of silicon oil (Aurosil 1000 cSt, Aurosil Plus 5000 cSt) on in vitro growth of common microorganisms causing endophthalmitis.
Materials and methods: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, multi-drug resistant (MDR) strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus flavus were prepared to 0.5 McFarland turbidity. The bacteria and fungi were inoculated into the silicone oils, brain heart infusion (BHI) broth for bacteria and Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) broth for fungi, respectively, and cultured aerobically for 30 days. From each sample, 10 μl was plated onto nutrient agar and potato dextrose agar (PDA) for testing growth of bacteria and fungi respectively. Cultures from specimens, overnight incubation, and CFU counting were repeated on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 14, 21, 24, and 30. Negative controls were brain heart infusion and physiologic saline as well as silicone oils without any inoculations.
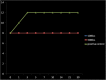
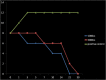
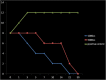
Results: All bacteria showed a decrease in CFUs by the fifth day and eliminated between 21 and 30 days in silicone oil. The silicon oil, irrespective of its viscosity, had only fungistatic effect up to 30 days. Colony-forming units of microorganisms remained stable in physiologic saline during the study. In BHI and Sabouraud broth, both bacteria and fungi showed a growth pattern that was compatible with the growth curve of microorganisms.
Conclusion: Medical-grade silicone oil used in ophthalmology exhibited in vitro bactericidal and fungistatic activity over 30 days. Insertion of silicone oil in vitrectomy for endophthalmitis, when required, could supplement the antimicrobial activities of intravitreal antibiotics in management of endophthalmitis.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity; Endophthalmitis; Silicone oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Kertes PJ, Peyman GA. Use of silicone oil in vitreous surgery. In: Peyman GA, Meffert SA, Conway MD, Chou F, editors. Vitreoretinal surgical techniques. Londres: Martin Dunitz; 2001. pp. 193–120.
-
- Parel JM, Milne P, Gaultier S, Jallet V, Villain F. Silicon oils: physicochemiproperties. In: Ryan SJ, editor. Retina. 4. St. Louis: Mosby; 2006. pp. 2191–2210.
-
- Bali E, Huyghe PH, Caspers L, Libert J. Vitrectomy and silicone oil in the treatment of acute endophthalmitis. Preliminary results Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 2003;288:9–14. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

