Downregulation of Brain Gα12 Attenuates Angiotensin II-Dependent Hypertension
- PMID: 31677381
- PMCID: PMC8205611
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpz176
Downregulation of Brain Gα12 Attenuates Angiotensin II-Dependent Hypertension
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin II (Ang II) activates central Angiotensin II type 1 receptors to increase blood pressure via multiple pathways. However, whether central Gα proteins contribute to Ang II-induced hypertension remains unknown. We hypothesized that Angiotensin II type 1 receptors couple with Gα12 and/or Gαq to produce sympatho-excitation and increase blood pressure and downregulation of these Gα-subunit proteins will attenuate Ang II-dependent hypertension.
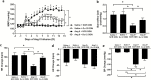
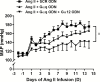
Methods and results: After chronic infusion of Ang II (s.c. 350 ng/kg/min) or vehicle for 2 weeks, Ang II evoked an increase in Gα12 expression, but not Gαq in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of Sprague-Dawley rats. In other studies, rats that received Ang II or vehicle infusion s.c. were simultaneously infused i.c.v. with a scrambled (SCR) or Gα12 oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN; 50 µg/day). Central Gα12 ODN infusion lowered mean blood pressure in Ang II infused rats compared with SCR ODN infusion (14-day peak; 133 ± 12 vs. 176 ± 11 mm Hg). Compared to the SCR ODN group, Ang II infused rats that received i.c.v. Gα12 ODN showed a greater increase in heart rate to atropine, an attenuated reduction in blood pressure to chlorisondamine, and an improved baroreflex sensitivity. In addition, central Gα12 and Gαq ODN pretreatment blunted the pressor response to an acute i.c.v. injection of Ang II (i.c.v., 200 ng).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that central Gα12 protein signaling pathways play an important role in the development of chronic Ang II-dependent hypertension in rats.
Keywords: Gα proteins; Gα12; Gαq; angiotensin II; blood pressure; brain; hypertension.
© American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd 2019. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Flaa A, Aksnes TA, Strand A, Kjeldsen SE. Complications of hypertension and the role of angiotensin receptor blockers in hypertension trials. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2007; 5:451–461. - PubMed
-
- Sasamura H, Mifune M, Nakaya H, Amemiya T, Hiraki T, Nishimoto I, Saruta T. Analysis of Galpha protein recognition profiles of angiotensin II receptors using chimeric Galpha proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2000; 170:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Mori J, Zhang L, Oudit GY, Lopaschuk GD. Impact of the renin-angiotensin system on cardiac energy metabolism in heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2013; 63:98–106. - PubMed
-
- Kim S, Iwao H. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated cardiovascular and renal diseases. Pharmacol Rev 2000; 52:11–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

