In silico Identification of a Molecular Circadian System With Novel Features in the Crustacean Model Organism Parhyale hawaiensis
- PMID: 31681024
- PMCID: PMC6813248
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01325
In silico Identification of a Molecular Circadian System With Novel Features in the Crustacean Model Organism Parhyale hawaiensis
Abstract
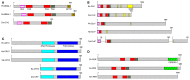
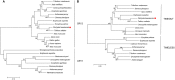
The amphipod Parhyale hawaiensis is a model organism of growing importance in the fields of evolutionary development and regeneration. A small, hardy marine crustacean that breeds year-round with a short generation time, it has simple lab culture requirements and an extensive molecular toolkit including the ability to generate targeted genetic mutant lines. Here we identify canonical core and regulatory clock genes using genomic and transcriptomic resources as a first step in establishing this species as a model in the field of chronobiology. The molecular clock of P. hawaiensis lacks orthologs of the canonical circadian genes cryptochrome 1 and timeless, in common with the mammalian system but in contrast to many arthropods including Drosophila melanogaster. Furthermore the predicted CLOCK peptide is atypical and CRY2 shows an extended 5' region of unknown function. These results appear to be shared by two other amphipod species.
Keywords: amphipod; circadian; clock; crustacean; genetics; hyalella; parhyale; talitrus.
Copyright © 2019 Hunt, Mallon and Rosato.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The crustacean model Parhyale hawaiensis.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2022;147:199-230. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.02.001. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35337450
-
De novo assembly and characterization of a maternal and developmental transcriptome for the emerging model crustacean Parhyale hawaiensis.BMC Genomics. 2011 Nov 25;12:581. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-581. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22118449 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and classification of cis-regulatory elements in the amphipod crustacean Parhyale hawaiensis.Development. 2022 Jun 1;149(11):dev200793. doi: 10.1242/dev.200793. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Development. 2022. PMID: 35608283
-
The amphipod crustacean Parhyale hawaiensis: An emerging comparative model of arthropod development, evolution, and regeneration.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2019 Sep;8(5):e355. doi: 10.1002/wdev.355. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31183976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-insect crustacean models in developmental genetics including an encomium to Parhyale hawaiensis.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Aug;39:149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27475080 Review.
Cited by
-
The circadian clock gene bmal1 is necessary for co-ordinated circatidal rhythms in the marine isopod Eurydice pulchra (Leach).PLoS Genet. 2023 Oct 19;19(10):e1011011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011011. eCollection 2023 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37856540 Free PMC article.
-
The diversity of opsins in Lake Baikal amphipods (Amphipoda: Gammaridae).BMC Ecol Evol. 2021 May 10;21(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12862-021-01806-9. BMC Ecol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33971810 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral circatidal rhythms require Bmal1 in Parhyale hawaiensis.Curr Biol. 2023 May 22;33(10):1867-1882.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.03.015. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 36977416 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of clock genes tracks daily and tidal time in brains of intertidal crustaceans Eurydice pulchra and Parhyale hawaiensis.Curr Biol. 2025 Jun 23;35(12):2802-2815.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2025.04.047. Epub 2025 May 8. Curr Biol. 2025. PMID: 40345195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews S. (2010). FastQC a Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online at: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

