Very Early MoCA Can Predict Functional Dependence at 3 Months After Stroke: A Longitudinal, Cohort Study
- PMID: 31681142
- PMCID: PMC6798188
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01051
Very Early MoCA Can Predict Functional Dependence at 3 Months After Stroke: A Longitudinal, Cohort Study
Abstract
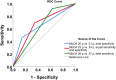
Introduction: After a stroke, cognitive impairment is commonly associated with poor functional outcomes. The primary aim of this study was to investigate if cognitive function, assessed with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) 36-48 h after stroke, could predict functional dependence 3 months later. The secondary aim was to identify an optimal threshold for the MoCA score that could predict functional dependence. Materials and Methods: This was a longitudinal cohort study. The research database from a stroke unit at the Sahlgrenska University Hospital was linked with the Swedish Stroke Register-Riksstroke. Cognitive function and activities of daily living (ADL) were assessed with the MoCA and the Barthel Index (BI), respectively, 36-48 h after stroke. Functional outcome 3 months after stroke was studied with the modified Rankin Scale. The predictive characteristics of the MoCA were investigated using logistic regression analyses. Receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC) were used for identifying the optimal cutoff score on the MoCA for predicting functional dependence. The MoCA score that had equal sensitivity and specificity was chosen as the optimal score for predicting functional dependence. Results: A total of 305 participants were included in the study (mean age: 68.8 years, n = 179 men). The MoCA quartiles were a significant predictor of functional dependence 3 months after stroke as an individual variable (p < 0.001, AUC = 0.72) and when adjusted for covariates such as age at stroke onset, living arrangement prior to stroke, and ADL measured with BI within 36-48 h after stroke (p = 0.01, AUC = 0.84). The MoCA score of ≤23 for impaired cognition had equal sensitivity and specificity for predicting functional dependence 3 months after stroke. Discussion and Conclusion: Cognitive function assessed with the MoCA within 36-48 h after stroke could predict functional dependence 3 months later. The participants with MoCA scores ≤23 for impaired cognition were more likely to be functionally dependent.
Keywords: ADL; acute stroke; cognitive function; global disability; modified Rankin Scale; sensitivity; specificity.
Copyright © 2019 Abzhandadze, Rafsten, Lundgren Nilsson, Palstam and Sunnerhagen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Feasibility of Cognitive Functions Screened With the Montreal Cognitive Assessment in Determining ADL Dependence Early After Stroke.Front Neurol. 2018 Aug 27;9:705. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00705. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30210432 Free PMC article.
-
Early MoCA predicts long-term cognitive and functional outcome and mortality after stroke.Neurology. 2018 Nov 13;91(20):e1838-e1850. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006506. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Neurology. 2018. PMID: 30333158
-
Association Between Early Cognitive Impairment and Midterm Functional Outcomes Among Chinese Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Longitudinal Study.Front Neurol. 2020 Feb 26;11:20. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00020. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32174878 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between 2 Measures of Cognitive Instrumental Activities of Daily Living and Their Relation to the Montreal Cognitive Assessment in Persons With Stroke.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017 Nov;98(11):2280-2287. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 May 4. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 28478128
-
Accuracy of the short-form Montreal Cognitive Assessment: Systematic review and validation.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019 Oct;34(10):1515-1525. doi: 10.1002/gps.5162. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31243810
Cited by
-
Predictors for self-reported feeling of depression three months after stroke: A longitudinal cohort study.J Rehabil Med. 2021 Mar 25;53(3):jrm00170. doi: 10.2340/16501977-2816. J Rehabil Med. 2021. PMID: 33739435 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to cognitive screening in acute stroke units.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 4;11(1):19621. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98853-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34608199 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Temporalis Muscle Mass with Early Cognitive Impairment in Older Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 15;12(12):4071. doi: 10.3390/jcm12124071. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373767 Free PMC article.
-
Montreal Cognitive Assessment of cognitive dysfunction after basal ganglia stroke.Acta Neurol Belg. 2022 Aug;122(4):881-884. doi: 10.1007/s13760-022-01967-4. Epub 2022 May 28. Acta Neurol Belg. 2022. PMID: 35624396 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Serum VEGF, IGF-1 and MMP-9 and Expression of Their Genes as Potential Prognostic Markers of Recovery in Post-Stroke Rehabilitation-A Prospective Observational Study.Brain Sci. 2023 May 23;13(6):846. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13060846. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37371326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riksstroke Stroke och TIA, Riksstrokes Årsrapport−2017 (Umeå: ) (2018).
-
- Danovska M, Peychinska D. Post-stroke cognitive impairment—Phenomenology and prognostic factors. J IMAB. (2012) 18:290–7. 10.5272/jimab.2012183.290 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

