Involvement of Ahr Pathway in Toxicity of Aflatoxins and Other Mycotoxins
- PMID: 31681212
- PMCID: PMC6798329
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02347
Involvement of Ahr Pathway in Toxicity of Aflatoxins and Other Mycotoxins
Abstract
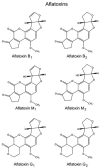
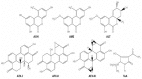
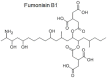
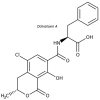
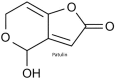
The purpose of this review is to present information about the role of activation of aflatoxins and other mycotoxins, of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) pathway. Aflatoxins and other mycotoxins are a diverse group of secondary metabolites that can be contaminants in a broad range of agricultural products and feeds. Some species of Aspergillus, Alternaria, Penicilium, and Fusarium are major producers of mycotoxins, some of which are toxic and carcinogenic. Several aflatoxins are planar molecules that can activate the AhR. AhR participates in the detoxification of several xenobiotic substances and activates phase I and phase II detoxification pathways. But it is important to recognize that AhR activation also affects differentiation, cell adhesion, proliferation, and immune response among others. Any examination of the effects of aflatoxins and other toxins that act as activators to AhR must consider the potential of the disruption of several cellular functions in order to extend the perception thus far about the toxic and carcinogenic effects of these toxins. There have been no Reviews of existing data between the relation of AhR and aflatoxins and this one attempts to give information precisely about this dichotomy.
Keywords: AFB1; Alternaria; Aspergillus; CYP1A1; alternariol (AOH).
Copyright © 2019 Arenas-Huertero, Zaragoza-Ojeda, Sánchez-Alarcón, Milić, Šegvić Klarić, Montiel-González and Valencia-Quintana.
Figures

References
-
- Ayed-Boussema I., Pascussi J. M., Maurel P., Bacha H., Hassen W. (2011). Activates pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor and aryl hydrocarbon receptor and corresponding phase I target genes mRNA in primary cultures of human hepatocytes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 31 79–87. 10.1016/j.etap.2010.09.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ayed-Boussema I., Pascussi J. M., Zaied C., Maurel P., Bacha H., Hassen W. (2012b). Ochratoxin A induces CYP3A4, 2B6, 3A5, 2C9, 1A1, and CYP1A2 gene expression in primary cultured human hepatocytes: a possible activation of nuclear receptors. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 35 71–80. 10.3109/01480545.2011.589438 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bacsi S. G., Reisz-Porszasz S., Hankinson O. (1995). Orientation of the heterodimeric aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor complex on its asymmetric DNA recognition sequence. Mol. Pharmacol. 47 432–438. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

