Red blood cell-derived nanoerythrosome for antigen delivery with enhanced cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 31681841
- PMCID: PMC6810293
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw6870
Red blood cell-derived nanoerythrosome for antigen delivery with enhanced cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
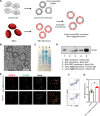
Erythrocytes or red blood cells (RBCs) represent a promising cell-mediated drug delivery platform due to their inherent biocompatibility. Here, we developed an antigen delivery system based on the nanoerythrosomes derived from RBCs, inspired by the splenic antigen-presenting cell targeting capacity of senescent RBCs. Tumor antigens were loaded onto the nanoerythrosomes by fusing tumor cell membrane-associated antigens with nanoerythrosomes. This tumor antigen-loaded nanoerythrosomes (nano-Ag@erythrosome) elicited antigen responses in vivo and, in combination with the anti-programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) blockade, inhibited the tumor growth in B16F10 and 4T1 tumor models. We also generated a tumor model showing that "personalized nano-Ag@erythrosomes" could be achieved by fusing RBCs and surgically removed tumors, which effectively reduced tumor recurrence and metastasis after surgery.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures



References
-
- Tang J., Yu J. X., Hubbard-Lucey V. M., Neftelinov S. T., Hodge J. P., Lin Y., The clinical trial landscape for PD1/PDL1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17, 854–855 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Postow M. A., Sidlow R., Hellmann M. D., Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 158–168 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

