Identification and Quantification of β-Sitosterol β-d-Glucoside of an Ethanolic Extract Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Agave angustifolia Haw
- PMID: 31683500
- PMCID: PMC6864453
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24213926
Identification and Quantification of β-Sitosterol β-d-Glucoside of an Ethanolic Extract Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Agave angustifolia Haw
Abstract
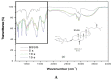
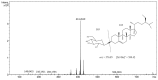
β-sitosterol β-d-glucoside (BSSG) was extracted from "piña" of the Agave angustifolia Haw plant by microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) with a KOH solution such as a catalyst and a conventional maceration method to determine the best technique in terms of yield, extraction time, and recovery. The quantification and characterization of BSSG were done by high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS). With an extraction time of 5 s by MAE, a higher amount of BSSG (124.76 mg of β-sitosterol β-d-glucoside/g dry weight of the extract) than those for MAE extraction times of 10 and 15 s (106.19 and 103.97 mg/g dry weight respectively) was shown. The quantification of BSSG in the extract obtained by 48 h of conventional maceration was about 4-5 times less (26.67 mg/g dry weight of the extract) than the yields reached by the MAE treatments. MAE achieved the highest amount of BSSG, in the shortest extraction time while preserving the integrity of the compound's structure.
Keywords: Agave angustifolia Haw; MAE; β-sitosterol β-d-glucoside.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Optimization of the Microwave-Assisted Ethanosolv Extraction of Lignocellulosic Compounds from the Bagasse of Agave angustifolia Haw Using the Response Methodology.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Apr 4;66(13):3533-3540. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04627. Epub 2018 Mar 23. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29513008
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of 3-O-[(6'-O-palmitoyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl sitosterol] from Agave angustifolia on ear edema in mice.Molecules. 2014 Sep 29;19(10):15624-37. doi: 10.3390/molecules191015624. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25268718 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of beta-sitosterol, stigmasterol and ergosterin in A. roxburghii using supercritical fluid extraction followed by liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization ion trap mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2007;21(18):3024-32. doi: 10.1002/rcm.3181. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2007. PMID: 17705339
-
Extraction, chemical characterization and biological activity determination of broccoli health promoting compounds.J Chromatogr A. 2013 Oct 25;1313:78-95. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.07.051. Epub 2013 Jul 16. J Chromatogr A. 2013. PMID: 23899380 Review.
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical characterization and evaluation of antioxidant, antimicrobial, antibiofilm and anticancer activities of ethyl acetate seed extract of Hydnocarpus laurifolia (Dennst) Sleummer.3 Biotech. 2022 Sep;12(9):215. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03267-3. Epub 2022 Aug 8. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35959166 Free PMC article.
-
UPLC-ESI-MS/MS Profiling and Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Antidiabetic, and Antiobesity Activities of the Non-Polar Fractions of Salvia hispanica L. Aerial Parts.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;12(5):1062. doi: 10.3390/plants12051062. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36903922 Free PMC article.
-
Moringa oleifera: An Updated Comprehensive Review of Its Pharmacological Activities, Ethnomedicinal, Phytopharmaceutical Formulation, Clinical, Phytochemical, and Toxicological Aspects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2098. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032098. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Agave Fructans on Changes in Chemistry, Morphology and Composition in the Biomass Growth of Milk Kefir Grains.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 13;11(6):1570. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061570. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37375072 Free PMC article.
-
β-Sitosterol Glucoside-Loaded Nanosystem Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 22;11(5):1023. doi: 10.3390/antiox11051023. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gentry H.S. Agaves of Continental North America. The University of Arizona Press; Tucson, AZ, USA: 1982. p. 670.
-
- García-Mendoza A. Sistemática y Distribución Actual de los Agave Smezcaleros. [(accessed on 23 May 2019)]; CONABIO. Fina Report. Project V029. Available online: http://www.conabio.gob.mx/institucion/cgi-bin/datos.cgi?Letras=V&Numero=....
-
- Hodgson W.C. Food Plants of the Sonoran Desert. The University of Arizona Press; Tucson, AZ, USA: 2001.
-
- Flores N.B., Araiza P.L.S. Estudios Sociales. Revista de Alimentación Contemporánea y Desarrollo Regional. CIAD; Hermosillo Sonora, Mexico: 2012. El mezcal en Sonora, México, más que una bebida espirituosa. Etnobotánica de Agave angustifolia Haw; pp. 173–197.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

