A Report on Fungal (1→3)-α-d-glucans: Properties, Functions and Application
- PMID: 31684030
- PMCID: PMC6864487
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24213972
A Report on Fungal (1→3)-α-d-glucans: Properties, Functions and Application
Abstract
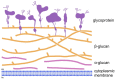
The cell walls of fungi are composed of glycoproteins, chitin, and α- and β-glucans. Although there are many reports on β-glucans, α-glucan polysaccharides are not yet fully understood. This review characterizes the physicochemical properties and functions of (1→3)-α-d-glucans. Particular attention has been paid to practical application and the effect of glucans in various respects, taking into account unfavourable effects and potential use. The role of α-glucans in plant infection has been proven, and collected facts have confirmed the characteristics of Aspergillus fumigatus infection associated with the presence of glucan in fungal cell wall. Like β-glucans, there are now evidence that α-glucans can also stimulate the immune system. Moreover, α-d-glucans have the ability to induce mutanases and can thus decompose plaque.
Keywords: (1→3)-α-d-glucans; cell walls; fungi; polysaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Grün C.H. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Utrecht; Utrecht, The Netherlands: 2003. Structure and Biosynthesis of Fungal α-Glucans.
-
- Wiater A., Pleszczynska M., Szczodrak J., Próchniak K. α-(1→3)-Glukany œciany komórkowej żółciaka siarkowego–Laetiporus sulphureus (Bull.: Fr.) Murrill–izolacja, charakterystyka i zastosowanie do indukcji syntezy. Biotechnologia. 2008;2:174–189.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical