A genome-wide DNA methylation signature for SETD1B-related syndrome
- PMID: 31685013
- PMCID: PMC6830011
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-019-0749-3
A genome-wide DNA methylation signature for SETD1B-related syndrome
Abstract
SETD1B is a component of a histone methyltransferase complex that specifically methylates Lys-4 of histone H3 (H3K4) and is responsible for the epigenetic control of chromatin structure and gene expression. De novo microdeletions encompassing this gene as well as de novo missense mutations were previously linked to syndromic intellectual disability (ID). Here, we identify a specific hypermethylation signature associated with loss of function mutations in the SETD1B gene which may be used as an epigenetic marker supporting the diagnosis of syndromic SETD1B-related diseases. We demonstrate the clinical utility of this unique epi-signature by reclassifying previously identified SETD1B VUS (variant of uncertain significance) in two patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

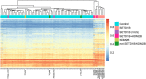

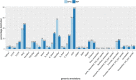


References
-
- Qiao Y, Tyson C, Hrynchak M, Lopez-Rangel E, Hildebrand J, Martell S, Fawcett C, Kasmara L, Calli K, Harvard C, et al. Clinical application of 2.7M Cytogenetics array for CNV detection in subjects with idiopathic autism and/or intellectual disability. Clin Genet. 2013;83(2):145–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01860.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Labonne JD, Lee KH, Iwase S, Kong IK, Diamond MP, Layman LC, Kim CH, Kim HG. An atypical 12q24.31 microdeletion implicates six genes including a histone demethylase KDM2B and a histone methyltransferase SETD1B in syndromic intellectual disability. Hum Genet. 2016;135(7):757–771. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1668-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

