Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab through 52 weeks in two phase 3, randomised, controlled clinical trials in patients with active radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (COAST-V and COAST-W)
- PMID: 31685553
- PMCID: PMC7025731
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216118
Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab through 52 weeks in two phase 3, randomised, controlled clinical trials in patients with active radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (COAST-V and COAST-W)
Erratum in
-
Correction: Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab through 52 weeks in two phase 3, randomised, controlled clinical trials in patients with active radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (COAST-V and COAST-W).Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79(6):e75. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216118corr1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32434813 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the efficacy and safety of ixekizumab for up to 52 weeks in two phase 3 studies of patients with active radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA) who were biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD)-naive (COAST-V) or tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)-experienced (COAST-W).
Methods: Adults with active r-axSpA were randomised 1:1:1:1 (n=341) to 80 mg ixekizumab every 2 (IXE Q2W) or 4 weeks (IXE Q4W), placebo (PBO) or 40 mg adalimumab Q2W (ADA) in COAST-V and 1:1:1 (n=316) to IXE Q2W, IXE Q4W or PBO in COAST-W. At week 16, patients receiving ixekizumab continued their assigned treatment; patients receiving PBO or ADA were rerandomised 1:1 to IXE Q2W or IXE Q4W (PBO/IXE, ADA/IXE) through week 52.
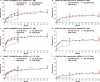
Results: In COAST-V, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society 40 (ASAS40) responses rates (intent-to-treat population, non-responder imputation) at weeks 16 and 52 were 48% and 53% (IXE Q4W); 52% and 51% (IXE Q2W); 36% and 51% (ADA/IXE); 19% and 47% (PBO/IXE). Corresponding ASAS40 response rates in COAST-W were 25% and 34% (IXE Q4W); 31% and 31% (IXE Q2W); 14% and 39% (PBO/IXE). Both ixekizumab regimens sustained improvements in disease activity, physical function, objective markers of inflammation, QoL, health status and overall function up to 52 weeks. Safety through 52 weeks of ixekizumab was consistent with safety through 16 weeks.
Conclusion: The significant efficacy demonstrated with ixekizumab at week 16 was sustained for up to 52 weeks in bDMARD-naive and TNFi-experienced patients. bDMARD-naive patients initially treated with ADA demonstrated further numerical improvements after switching to ixekizumab. Safety findings were consistent with the known safety profile of ixekizumab.
Trial registration number: NCT02696785/NCT02696798.
Keywords: DMARDs (biologic); ankylosing spondylitis; spondyloarthritis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MD has served as a consultant and received research grants from AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer and UCB Pharma. JC-CW has served as a consultant and/or speaker and/or has received research grants from Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, TSH Taiwan and UCB Pharma. RL has served as a consultant and/or advisor and/or has received research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Galapagos, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Pharma. RL is the director of Rheumatology Consultancy BV, a company that was indirectly contracted by Eli Lilly and Company to perform read services for the COAST program. JS has served as a consultant and/or speaker for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB Pharma. XB has served as a consultant and/or has received research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB Pharma. FVdB has served as a consultant and/or speaker and/or has received research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi and UCB Pharma. WPM has served as a consultant and/or received honoraria and/or research/educational grants from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Pharma, and is Chief Medical Officer of CARE Arthritis Limited. JE has served as a consultant and/or received research grants from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda and UCB Pharma. JAW has been a consultant and/or received research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Pharma. AD has been a consultant and/or received research support from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, Glaxo Smith & Klein, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Pharma. DvdH has been a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Daiichi, Eli Lilly and Company, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda and UCB Pharma and is a Director of Imaging Rheumatology BV. TT has been a consultant and speaker for AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Novartis, Pfizer and Takeda. XL, FZ, CCB, GG and HC are current employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. LSG has been a consultant and/or received research grants/support from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly and Company, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Pharma.
Figures


References
-
- Boonen A, van der Linden SM. The burden of ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol Suppl 2006;78:4–11. - PubMed
-
- Ward MM, Deodhar A, Akl EA, et al. . American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis association of America/Spondyloarthritis research and treatment network 2015 recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2016;68:151–66. 10.1002/acr.22708 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

