Growth and Distribution of Child Psychiatrists in the United States: 2007-2016
- PMID: 31685696
- PMCID: PMC6889947
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2019-1576
Growth and Distribution of Child Psychiatrists in the United States: 2007-2016
Abstract
Background: Historically, there has been a shortage of child psychiatrists in the United States, undermining access to care. This study updated trends in the growth and distribution of child psychiatrists over the past decade.
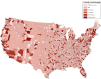
Methods: Data from the Area Health Resource Files were used to compare the number of child psychiatrists per 100 000 children ages 0 to 19 between 2007 and 2016 by state and county. We also examined sociodemographic characteristics associated with the density of child psychiatrists at the county level over this period using negative binomial multivariable models.
Results: From 2007 to 2016, the number of child psychiatrists in the United States increased from 6590 to 7991, a 21.3% gain. The number of child psychiatrists per 100 000 children also grew from 8.01 to 9.75, connoting a 21.7% increase. County- and state-level growth varied widely, with 6 states observing a decline in the ratio of child psychiatrists (ID, IN, KS, ND, SC, and SD) and 6 states increasing by >50% (AK, AR, NH, NV, OK, and RI). Seventy percent of counties had no child psychiatrists in both 2007 and 2016. Child psychiatrists were significantly more likely to practice in high-income counties (P < .001), counties with higher levels of postsecondary education (P < .001), and metropolitan counties compared with those adjacent to metropolitan regions (P < .05).
Conclusions: Despite the increased ratio of child psychiatrists per 100 000 children in the United States over the past decade, there remains a dearth of child psychiatrists, particularly in parts of the United States with lower levels of income and education.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
Meeting the Demand for Pediatric Mental Health Care.Pediatrics. 2019 Dec;144(6):e20192646. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2646. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Pediatrics. 2019. PMID: 31685697 No abstract available.
References
-
- Olfson M, Blanco C, Wang S, Laje G, Correll CU. National trends in the mental health care of children, adolescents, and adults by office-based physicians. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014;71(1):81–90 - PubMed
-
- Kogan MD, Blumberg SJ, Schieve LA, et al. . Prevalence of parent-reported diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder among children in the US, 2007. Pediatrics. 2009;124(5):1395–1403 - PubMed
-
- Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. . Screening for autism spectrum disorder in young children: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;315(7):691–696 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

