Nanohydroxyapatite Reinforced Chitosan Composite Hydrogel with Tunable Mechanical and Biological Properties for Cartilage Regeneration
- PMID: 31685836
- PMCID: PMC6828803
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-52042-7
Nanohydroxyapatite Reinforced Chitosan Composite Hydrogel with Tunable Mechanical and Biological Properties for Cartilage Regeneration
Abstract
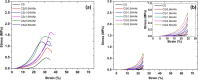
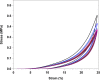
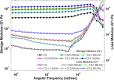
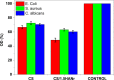
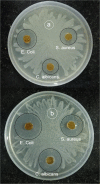
With the continuous quest of developing hydrogel for cartilage regeneration with superior mechanobiological properties are still becoming a challenge. Chitosan (CS) hydrogels are the promising implant materials due to an analogous character of the soft tissue; however, their low mechanical strength and durability together with its lack of integrity with surrounding tissues hinder the load-bearing application. This can be solved by developing a composite chitosan hydrogel reinforced with Hydroxyapatite Nanorods (HANr). The objective of this work is to develop and characterize (physically, chemically, mechanically and biologically) the composite hydrogels loaded with different concentration of hydroxyapatite nanorod. The concentration of hydroxyapatite in the composite hydrogel was optimized and it was found that, reinforcement modifies the hydrogel network by promoting the secondary crosslinking. The compression strength could reach 1.62 ± 0.02 MPa with a significant deformation of 32% and exhibits time-dependent, rapid self-recoverable and fatigue resistant behavior based on the cyclic loading-unloading compression test. The storage modulus value can reach nearly 10 kPa which is needed for the proposed application. Besides, composite hydrogels show an excellent antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus bacteria's and Candida albicans fungi and their cytocompatibility towards L929 mouse fibroblasts provide a potential pathway to developing a composite hydrogel for cartilage regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ren, X. et al. Aligned porous fibrous membrane with a biomimetic surface to accelerate cartilage regeneration. Chemical Engineering Journal, 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.271 (2019).
-
- Tardy N, Maqdes A, Boisrenoult P, Beaufils P, Oger P. Small diameter metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty at 13 years - a follow-up study. Orthopaedics and Traumatology: Surgery and Research. 2015;101:929–936. - PubMed
-
- Puppi D, Chiellini F, Piras AM, Chiellini E. Polymeric materials for bone and cartilage repair. Progress in Polymer Science. 2010;35:403–440. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.01.006. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

