Individualized home-monitoring of disease activity in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease can be recommended in clinical practice: A randomized-clinical trial
- PMID: 31686770
- PMCID: PMC6824278
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6158
Individualized home-monitoring of disease activity in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease can be recommended in clinical practice: A randomized-clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The optimal way to home-monitor patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) for disease progression or relapse remains to be found.
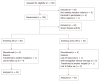
Aim: To determine whether an electronic health (eHealth) screening procedure for disease activity in IBD should be implemented in clinical practice, scheduled every third month (3M) or according to patient own decision, on demand (OD).
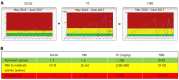
Methods: Adult IBD patients were consecutively randomized to 1-year open-label eHealth interventions (3M vs OD). Both intervention arms were screening for disease activity, quality of life and fatigue and were measuring medical compliance with the constant care web-application according to the screening interventions OD or 3M. Disease activity was assessed using home measured fecal calprotectin (FC) and a disease activity score.
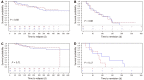
Results: In total, 102 patients were randomized (n = 52/50 3M/OD) at baseline, and 88 patients completed the 1-year study (n = 43 3M; n = 45 OD). No difference in the two screening procedures could be found regarding medical compliance (P = 0.58), fatigue (P = 0.86), quality of life (P = 0.17), mean time spent in remission (P > 0.32), overall FC relapse rates (P = 0.49), FC disease courses (P = 0.61), FC time to a severe relapse (P = 0.69) and remission (P = 0.88) during 1 year. Median (interquartile range) numbers of FC home-monitoring test-kits used per patient were significantly different, 3M: 6.0 (5.0-8.0) and OD: 4.0 (2.0-9.0), P = 0.04.
Conclusion: The two eHealth screening procedures are equally good in capturing a relapse and bringing about remission. However, the OD group used fewer FC home test-kits per patient. Individualized screening procedures can be recommended for adult IBD patients in clinical web-practice.
Keywords: Disease activity; Electronic health; Inflammatory bowel disease; Screening.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Ankersen DV has received grants from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Crohn Colitis patient society Denmark, North Zealand University Hospital and non-financial support from Calpro AS; Weimers P has received grants from Ferring lægemidler and Tillotts Pharma AG as well as non-financial support from Janssen-Cilag A/S, Calpro AS, and Vifor Pharma Nordiska AB; Marker D has received non-financial support from Calpro AS and Pharmacosmos; Bennedsen M has received other financial support from AbbVie, Tillotts, Takeda, MSD and Pfizer; Saboori S has received non-financial support from Janssen-Cilag and Salofalk; Paridaens K is an employee of Ferring Pharmaceuticals; Burisch J has received grants from AbbVie, Takeda, Tillotts Pharma and personal fees from AbbVie, Janssen-Cilag, Celgene, Samsung Bioepis, MSD, Pfizer and Takeda; Munkholm P has none to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Langholz E. Ulcerative colitis. An epidemiological study based on a regional inception cohort, with special reference to disease course and prognosis. Dan Med Bull. 1999;46:400–415. - PubMed
-
- Munkholm P. Crohn's disease--occurrence, course and prognosis. An epidemiologic cohort-study. Dan Med Bull. 1997;44:287–302. - PubMed
-
- Burisch J, Kiudelis G, Kupcinskas L, Kievit HAL, Andersen KW, Andersen V, Salupere R, Pedersen N, Kjeldsen J, D'Incà R, Valpiani D, Schwartz D, Odes S, Olsen J, Nielsen KR, Vegh Z, Lakatos PL, Toca A, Turcan S, Katsanos KH, Christodoulou DK, Fumery M, Gower-Rousseau C, Chetcuti Zammit S, Ellul P, Eriksson C, Halfvarson J, Magro FJ, Duricova D, Bortlik M, Fernandez A, Hernández V, Myers S, Sebastian S, Oksanen P, Collin P, Goldis A, Misra R, Arebi N, Kaimakliotis IP, Nikuina I, Belousova E, Brinar M, Cukovic-Cavka S, Langholz E, Munkholm P Epi-IBD group. Natural disease course of Crohn's disease during the first 5 years after diagnosis in a European population-based inception cohort: an Epi-IBD study. Gut. 2018;0:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Burisch J, Jess T, Martinato M, Lakatos PL ECCO -EpiCom. The burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Europe. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7:322–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

