Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition enhances anti-inflammatory and antioxidative processes, modulates microglia polarization, and promotes recovery after ischemic stroke
- PMID: 31686827
- PMCID: PMC6800549
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S210403
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition enhances anti-inflammatory and antioxidative processes, modulates microglia polarization, and promotes recovery after ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background: Ischemic stroke triggers inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in the brain, and microglia polarization affects the degree of neuroinflammation. It has been reported that the inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) activity protects brain tissue. However, the anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of sEH inhibition in the ischemic brain are not fully understood. This study aimed to investigate the effects of a selective sEH inhibitor, 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid (AUDA), after ischemic stroke.
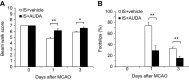
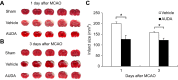
Methods: Adult male rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) were administered with AUDA or a vehicle. Behavioral outcome, infarct volume, microglia polarization, and gene expression were assessed.
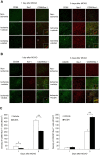
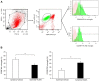
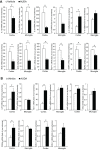
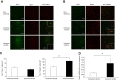
Results: Rats treated with AUDA showed better behavioral outcomes and smaller infarct volumes after MCAO. After AUDA treatment, a reduction of M1 microglia and an increase of M2 microglia occurred at the ischemic cortex of rats. Additionally, there was an increase in the mRNA expressions of antioxidant enzymes and anti-inflammatory interleukin-10, and pro-inflammatory mediators were decreased after AUDA administration. Heme oxygenase-1 was mainly expressed by neurons, and AUDA was found to improve the survival of neurons.
Conclusion: The results of this study provided novel and significant insights into how AUDA can improve outcomes and modulate inflammation and oxidative stress after ischemic stroke.
Keywords: anti-inflammation; antioxidant; ischemic stroke; microglia polarization; middle cerebral artery occlusion; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
© 2019 Yeh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor Ameliorates Olfactory Dysfunction, Modulates Microglia Polarization, and Attenuates Neuroinflammation after Ischemic Brain Injury.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 17;19(1):54. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10155-5. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39417923
-
Genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase reduces brain damage and attenuates neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Nov 25;14(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-1005-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 29178914 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates monocyte/macrophage polarization and improves neurological outcome in a rat model of ischemic stroke.Neuroreport. 2019 May 22;30(8):567-572. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001248. Neuroreport. 2019. PMID: 30950936
-
An epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)dodecanoic acid (AUDA), reduces ischemic cerebral infarct size in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005 Dec;46(6):842-8. doi: 10.1097/01.fjc.0000189600.74157.6d. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16306811 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase: a novel therapeutic target in stroke.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007 Dec;27(12):1931-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600494. Epub 2007 Apr 18. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. PMID: 17440491 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multimodal Optical Imaging to Investigate Spatiotemporal Changes in Cerebrovascular Function in AUDA Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Jun 3;15:655305. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.655305. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34149359 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Response of the Brain Free Oxylipin Profile to Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 28;15(5):1214. doi: 10.3390/nu15051214. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904213 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial pro-inflammatory mechanisms induced by monomeric C-reactive protein are counteracted by soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 May 16;155:114644. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114644. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40215773 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition improves cognitive function and parenchymal artery dilation in a hypertensive model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.Microcirculation. 2021 Jan;28(1):e12653. doi: 10.1111/micc.12653. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Microcirculation. 2021. PMID: 32767848 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Improves Learning and Memory Impairment in Rats with Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Microglia/Macrophage M2 Polarization Through Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 26;18:2925-2941. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S504670. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40026308 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

