A Functional Role of GAS6/TAM in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Progression Implicates AXL as Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 31689560
- PMCID: PMC7013198
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.10.010
A Functional Role of GAS6/TAM in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Progression Implicates AXL as Therapeutic Target
Abstract
Background and aims: GAS6 signaling, through the TAM receptor tyrosine kinases AXL and MERTK, participates in chronic liver pathologies. Here, we addressed GAS6/TAM involvement in Non-Alcoholic SteatoHepatitis (NASH) development.
Methods: GAS6/TAM signaling was analyzed in cultured primary hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and Kupffer cells (KCs). Axl-/-, Mertk-/- and wild-type C57BL/6 mice were fed with Chow, High Fat Choline-Deficient Methionine-Restricted (HFD) or methionine-choline-deficient (MCD) diet. HSC activation, liver inflammation and cytokine/chemokine production were measured by qPCR, mRNA Array analysis, western blotting and ELISA. GAS6, soluble AXL (sAXL) and MERTK (sMERTK) levels were analyzed in control individuals, steatotic and NASH patients.
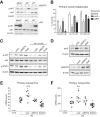
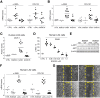
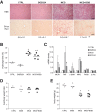
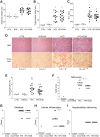
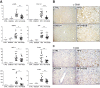
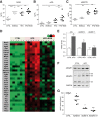
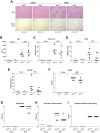
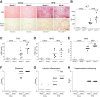
Results: In primary mouse cultures, GAS6 or MERTK activation protected primary hepatocytes against lipid toxicity via AKT/STAT-3 signaling, while bemcentinib (small molecule AXL inhibitor BGB324) blocked AXL-induced fibrogenesis in primary HSCs and cytokine production in LPS-treated KCs. Accordingly; bemcentinib diminished liver inflammation and fibrosis in MCD- and HFD-fed mice. Upregulation of AXL and ADAM10/ADAM17 metalloproteinases increased sAXL in HFD-fed mice. Transcriptome profiling revealed major reduction in fibrotic- and inflammatory-related genes in HFD-fed mice after bemcentinib administration. HFD-fed Mertk-/- mice exhibited enhanced NASH, while Axl-/- mice were partially protected. In human serum, sAXL levels augmented even at initial stages, whereas GAS6 and sMERTK increased only in cirrhotic NASH patients. In agreement, sAXL increased in HFD-fed mice before fibrosis establishment, while bemcentinib prevented liver fibrosis/inflammation in early NASH.
Conclusion: AXL signaling, increased in NASH patients, promotes fibrosis in HSCs and inflammation in KCs, while GAS6 protects cultured hepatocytes against lipotoxicity via MERTK. Bemcentinib, by blocking AXL signaling and increasing GAS6 levels, reduces experimental NASH, revealing AXL as an effective therapeutic target for clinical practice.
Keywords: Bemcentinib (BGB324); GAS6/TAM Signaling; Hepatic Stellate Cells; Liver Fibrosis; Liver Inflammation.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Staging NAFLD: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of TAM Signaling.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;9(3):545-546. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.11.014. Epub 2019 Dec 25. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31881182 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Younossi Z.M., Loomba R., Rinella M.E., Bugianesi E., Marchesini G., Neuschwander-Tetri B.A., Serfaty L., Negro F., Caldwell S.H., Ratziu V., Corey K.E., Friedman S.L., Abdelmalek M.F., Harrison S.A., Sanyal A.J., Lavine J.E., Mathurin P., Charlton M.R., Chalasani N.P., Anstee Q.M., Kowdley K.V., George J., Goodman Z.D., Lindor K. Current and future therapeutic regimens for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2018;68:361–371. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rinella M.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015;313:2263–2273. - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z.M., Koenig A.B., Abdelatif D., Fazel Y., Henry L., Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Schuppan D., Surabattula R., Wang X.Y. Determinants of fibrosis progression and regression in NASH. J Hepatol. 2018;68:238–250. - PubMed
-
- Ratziu V., Harrison S.A., Francque S., Bedossa P., Lehert P., Serfaty L., Romero-Gomez M., Boursier J., Abdelmalek M., Caldwell S., Drenth J., Anstee Q.M., Hum D., Hanf R., Roudot A., Megnien S., Staels B., Sanyal A., Group G.-I.S. Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and -delta, induces resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis without fibrosis worsening. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1147–1159.e5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

