Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
- PMID: 31689999
- PMCID: PMC6893586
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11112657
Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
Abstract
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic disease mediated by the immune system and is characterized by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. One of the possible treatments for this pathology is a change in the type of diet, of which enteral nutrition (EN) is one. This study is to understand how the use of EN can affect the adult population diagnosed with IBD. We conducted a systematic review, meta-analysis, and a meta-regression. On the different databases (MEDLINE, Scopus, Cochrane, LILACS, CINAHL, WOS), we found 363 registers with an accuracy of 12% (44 registers). After a full-text review, only 30 research studies were selected for qualitative synthesis and 11 for meta-analysis and meta-regression. The variables used were Crohn's disease activity index (CDAI), C-reactive protein (CRP), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). EN has been shown to have efficacy for the treatment of Crohn's disease and is compatible with other medicines. As for the CDAI or rates of remission, there were no differences between enteral and parenteral nutrition. Polymeric formulas have shown better results with respect to the CRP. The long-term treatment could dilute the good CDAI results that are obtained at the start of the EN treatment.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; enteral nutrition; inflammatory bowel diseases; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

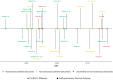
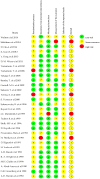
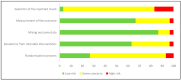




References
-
- Coward S., Clement F., Benchimol E.I., Bernstein C.N., Avina-Zubieta J.A., Bitton A., Carroll M.W., Hazlewood G., Jacobson K., Jelinski S., et al. Past and Future Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Based on Modeling of Population-Based Data. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1345–1353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ng S.C., Shi H.Y., Hamidi N., Underwood F.E., Tang W., Benchimol E.I., Panaccione R., Ghosh S., Wu J.C.Y., Chan F.K.L., et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390:2769–2778. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

