Hepatic stearoyl CoA desaturase 1 deficiency increases glucose uptake in adipose tissue partially through the PGC-1α-FGF21 axis in mice
- PMID: 31690632
- PMCID: PMC6926457
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009868
Hepatic stearoyl CoA desaturase 1 deficiency increases glucose uptake in adipose tissue partially through the PGC-1α-FGF21 axis in mice
Abstract
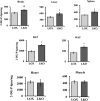
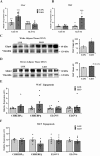
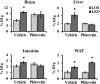
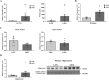
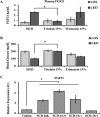
Increased carbohydrate consumption increases hepatic de novo lipogenesis, which has been linked to the development of chronic metabolic diseases, including obesity, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance. Stearoyl CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1) is a critical lipogenic enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of two monounsaturated fatty acids, oleate and palmitoleate, from the saturated fatty acids stearate and palmitate, respectively. SCD1-deficient mouse models are protected against diet-induced adiposity, hepatic steatosis, and hyperglycemia. However, the mechanism of this protection by SCD1 deficiency is unclear. Using liver-specific SCD1 knockout (LKO) mice fed a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet, we show that hepatic SCD1 deficiency increases systemic glucose uptake. Hepatic SCD1 deficiency enhanced glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) expression in the liver and also up-regulated GLUT4 and adiponectin expression in adipose tissue. The enhanced glucose uptake correlated with increased liver expression and elevated plasma levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), a hepatokine known to increase systemic insulin sensitivity and regulate whole-body lipid metabolism. Feeding LKO mice a triolein-supplemented but not tristearin-supplemented high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet reduced FGF21 expression and plasma levels. Consistently, SCD1 inhibition in primary hepatocytes induced FGF21 expression, which was repressed by treatment with oleate but not palmitoleate. Moreover, deletion of the transcriptional coactivator PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) reduced hepatic and plasma FGF21 and white adipocyte tissue-specific GLUT4 expression and raised plasma glucose levels in LKO mice. These results suggest that hepatic oleate regulates glucose uptake in adipose tissue either directly or partially by modulating the hepatic PGC-1α-FGF21 axis.
Keywords: adiponectin; carbohydrate metabolism; fibroblast growth factor (FGF); glucose metabolism; glucose transport; glucose transporters; heptokine-FGF21; insulin sensitivity; lipid metabolism; lipid signaling; liver; liver metabolism; liver–adipocyte cross-talk; monounsaturated fatty acids; obesity; stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1.
© 2019 Aljohani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health
Figures
References
-
- Bagby S. P. (2004) Obesity-initiated metabolic syndrome and the kidney: a recipe for chronic kidney disease? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15, 2775–2791 10.1097/01.ASN.0000141965.28037.EE - DOI - PubMed
-
- Higuchi N., Kato M., Shundo Y., Tajiri H., Tanaka M., Yamashita N., Kohjima M., Kotoh K., Nakamuta M., Takayanagi R., and Enjoji M. (2008) Liver X receptor in cooperation with SREBP-1c is a major lipid synthesis regulator in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 38, 1122–1129 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2008.00382.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yew Tan C., Virtue S., Murfitt S., Roberts L. D., Robert L. D., Phua Y. H., Dale M., Griffin J. L., Tinahones F., Scherer P. E., and Vidal-Puig A. (2015) Adipose tissue fatty acid chain length and mono-unsaturation increases with obesity and insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 5, 18366 10.1038/srep18366 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

