Neural stem cell transplantation therapy for brain ischemic stroke: Review and perspectives
- PMID: 31692854
- PMCID: PMC6828598
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i10.817
Neural stem cell transplantation therapy for brain ischemic stroke: Review and perspectives
Abstract
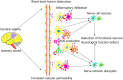
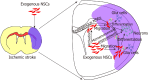
Brain ischemic stroke is one of the most common causes of death and disability, currently has no efficient therapeutic strategy in clinic. Due to irreversible functional neurons loss and neural tissue injury, stem cell transplantation may be the most promising treatment approach. Neural stem cells (NSCs) as the special type of stem cells only exist in the nervous system, can differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, and have the abilities to compensate insufficient endogenous nerve cells and improve the inflammatory microenvironment of cell survival. In this review, we focused on the important role of NSCs therapy for brain ischemic stroke, mainly introduced the methods of optimizing the therapeutic efficacy of NSC transplantation, such as transfection and overexpression of specific genes, pretreatment of NSCs with inflammatory factors, and co-transplantation with cytokines. Next, we discussed the potential problems of NSC transplantation which seriously limited their rapid clinical transformation and application. Finally, we expected a new research topic in the field of stem cell research. Based on the bystander effect, exosomes derived from NSCs can overcome many of the risks and difficulties associated with cell therapy. Thus, as natural seed resource of nervous system, NSCs-based cell-free treatment is a newly therapy strategy, will play more important role in treating ischemic stroke in the future.
Keywords: Cytokines; Exosomes; Ischemic stroke; Neural stem cells; Transplantation.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BDNF Pretreatment of Human Embryonic-Derived Neural Stem Cells Improves Cell Survival and Functional Recovery After Transplantation in Hypoxic-Ischemic Stroke.Cell Transplant. 2015;24(12):2449-61. doi: 10.3727/096368914X679354. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Cell Transplant. 2015. PMID: 24594369
-
NSC-derived exosomes enhance therapeutic effects of NSC transplantation on cerebral ischemia in mice.Elife. 2023 Apr 27;12:e84493. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84493. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37104115 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin Preconditioning of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Stem Cells Promotes Their Engraftment and Improves Post-Stroke Regeneration and Recovery.Stem Cells Dev. 2018 Aug 15;27(16):1085-1096. doi: 10.1089/scd.2018.0055. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Stem Cells Dev. 2018. PMID: 29893190
-
Neural Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles: key Players in Ischemic Stroke Therapy - A Comprehensive Literature Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 May 14;19:4279-4295. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S451642. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38766658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural Stem Cells Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: Progress and Challenges.Transl Stroke Res. 2022 Oct;13(5):665-675. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-00984-y. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Transl Stroke Res. 2022. PMID: 35032307 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Pathogenesis of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Strokes: Background and Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 7;25(12):6297. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126297. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano biomaterials based strategies for enhanced brain targeting in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: an up-to-date perspective.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Dec 13;21(1):477. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02250-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 38087359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem-Cell-Based Therapy: The Celestial Weapon against Neurological Disorders.Cells. 2022 Nov 2;11(21):3476. doi: 10.3390/cells11213476. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transplantation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Neural Stem Cells Pretreated with Neuregulin1β Ameliorate Cerebral Ischemic Reperfusion Injury in Rats.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 10;12(3):428. doi: 10.3390/biom12030428. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327620 Free PMC article.
-
Co-administration of extracellular matrix-based biomaterials with neural stem cell transplantation for treatment of central nervous system injury.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 15;17:1177040. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1177040. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37255752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson L, Truelsen T, O'Donnell M, Venketasubramanian N, Barker-Collo S, Lawes CM, Wang W, Shinohara Y, Witt E, Ezzati M, Naghavi M, Murray C Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2010 (GBD 2010) and the GBD Stroke Experts Group. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2014;383:245–254. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Langhorne P, Bernhardt J, Kwakkel G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet. 2011;377:1693–1702. - PubMed
-
- Fisher M. New approaches to neuroprotective drug development. Stroke. 2011;42:S24–S27. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa M, Zhang JH, Nanda A, Granger DN. Inflammatory responses to ischemia and reperfusion in the cerebral microcirculation. Front Biosci. 2004;9:1339–1347. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

