Superinfection of hepatitis A virus in hepatocytes infected with hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 31692913
- PMCID: PMC6818197
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.32795
Superinfection of hepatitis A virus in hepatocytes infected with hepatitis B virus
Abstract
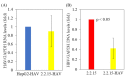
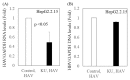
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection is a major cause of acute hepatitis including acute liver failure. Hepatitis B infection (HBV) occurs worldwide, with the highest rates in Asian and African countries, and there are several reports that HAV infection may have a more severe clinical course in patients with chronic HBV infection. We previously demonstrated that Japanese miso extracts have inhibitory effects on HAV replication. In the present study, we examined the replication of HAV and HBV in a hepatocyte superinfection model and the inhibitory effects of Japanese miso extracts on both viruses. According to the results, HAV infection inhibited HBV replication in superinfected hepatocytes, and Japanese rice-koji miso extracts had inhibitory effects on HAV replication. Our findings provide useful information for clinicians in managing HAV infection in patients with chronic HBV infection.
Keywords: HAV; HBV; dual infection; miso extracts; rice koji.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Vento S, Garofano T, Renzini C. et al. Fulminant hepatitis associated with hepatitis A virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:286–90. - PubMed
-
- Spada E, Genovese D, Tosti ME. et al. An outbreak of hepatitis A virus infection with a high case-fatality rate among injecting drug users. J Hepatol. 2005;43:958–64. - PubMed
-
- Sainokami S, Abe K, Ishikawa K. et al. Influence of load of hepatitis A virus on disease severity and its relationship with clinical manifestations in patients with hepatitis A. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:1165–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

