The Kidney Failure Risk Equation for prediction of end stage renal disease in UK primary care: An external validation and clinical impact projection cohort study
- PMID: 31693662
- PMCID: PMC6834237
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002955
The Kidney Failure Risk Equation for prediction of end stage renal disease in UK primary care: An external validation and clinical impact projection cohort study
Erratum in
-
Correction: The Kidney Failure Risk Equation for prediction of end stage renal disease in UK primary care: An external validation and clinical impact projection cohort study.PLoS Med. 2020 Jul 24;17(7):e1003313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003313. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32706776 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The Kidney Failure Risk Equation (KFRE) uses the 4 variables of age, sex, urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to predict the risk of end stage renal disease (ESRD), i.e., the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant, within 2 and 5 years. Currently, national guideline writers in the UK and other countries are evaluating the role of the KFRE in renal referrals from primary care to secondary care, but the KFRE has had limited external validation in primary care. The study's objectives were therefore to externally validate the KFRE's prediction of ESRD events in primary care, perform model recalibration if necessary, and assess its projected impact on referral rates to secondary care renal services.
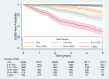
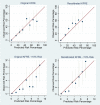
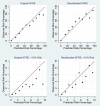
Methods and findings: Individuals with 2 or more Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) eGFR values < 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 more than 90 days apart and a urine ACR or protein-to-creatinine ratio measurement between 1 December 2004 and 1 November 2016 were included in the cohort. The cohort included 35,539 (5.6%) individuals (57.5% female, mean age 75.9 years, median CKD-EPI eGFR 51 ml/min/1.73 m2, median ACR 3.2 mg/mmol) from a total adult practice population of 630,504. Overall, 176 (0.50%) and 429 (1.21%) ESRD events occurred within 2 and 5 years, respectively. Median length of follow-up was 4.7 years (IQR 2.8 to 6.6). Model discrimination was excellent for both 2-year (C-statistic 0.932, 95% CI 0.909 to 0.954) and 5-year (C-statistic 0.924, 95% 0.909 to 0.938) ESRD prediction. The KFRE overpredicted risk in lower (<20%) risk groups. Reducing the model's baseline risk improved calibration for both 2- and 5-year risk for lower risk groups, but led to some underprediction of risk in higher risk groups. Compared to current criteria, using referral criteria based on a KFRE-calculated 5-year ESRD risk of ≥5% and/or an ACR of ≥70 mg/mmol reduced the number of individuals eligible for referral who did not develop ESRD, increased the likelihood of referral eligibility in those who did develop ESRD, and referred the latter at a younger age and with a higher eGFR. The main limitation of the current study is that the cohort is from one region of the UK and therefore may not be representative of primary care CKD care in other countries.
Conclusions: In this cohort, the recalibrated KFRE accurately predicted the risk of ESRD at 2 and 5 years in primary care. Its introduction into primary care for referrals to secondary care renal services may lead to a reduction in unnecessary referrals, and earlier referrals in those who go on to develop ESRD. However, further validation studies in more diverse cohorts of the clinical impact projections and suggested referral criteria are required before the latter can be clinically implemented.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: Data from the Nene Clinical Commissioning Group, Northamptonshire, are currently used by the CKD Prognosis Consortium (CKD-PC) for ongoing analysis. At the time of the development of KFRE by CKD-PC the authors were not working in collaboration with CKD-PC. No member of the CKD-PC was involved in the development, analysis or drafting of the current manuscript. The authors declare that there are no other relevant competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Astor BC, Matsushita K, Gansevoort RT, Van Der Velde M, Woodward M, Levey AS, et al. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with mortality and end-stage renal disease. A collaborative meta-analysis of kidney disease population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011;79(12):1331–40. 10.1038/ki.2010.550 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;375(9731):2073–81. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60674-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

