DoubletDecon: Deconvoluting Doublets from Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Data
- PMID: 31693907
- PMCID: PMC6983270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.09.082
DoubletDecon: Deconvoluting Doublets from Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Data
Abstract
Methods for single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) have greatly advanced in recent years. While droplet- and well-based methods have increased the capture frequency of cells for scRNA-seq, these technologies readily produce technical artifacts, such as doublet cell captures. Doublets occurring between distinct cell types can appear as hybrid scRNA-seq profiles, but do not have distinct transcriptomes from individual cell states. We introduce DoubletDecon, an approach that detects doublets with a combination of deconvolution analyses and the identification of unique cell-state gene expression. We demonstrate the ability of DoubletDecon to identify synthetic, mixed-species, genetic, and cell-hashing cell doublets from scRNA-seq datasets of varying cellular complexity with a high sensitivity relative to alternative approaches. Importantly, this algorithm prevents the prediction of valid mixed-lineage and transitional cell states as doublets by considering their unique gene expression. DoubletDecon has an easy-to-use graphical user interface and is compatible with diverse species and unsupervised population detection algorithms.
Keywords: RNA-seq; artifact detection; bioinformatics; deconvolution; doublet; multiplet; single-cell RNA-seq.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
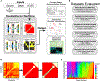
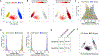
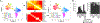


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

