Epitranscriptomic marks: Emerging modulators of RNA virus gene expression
- PMID: 31694072
- PMCID: PMC7169815
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1576
Epitranscriptomic marks: Emerging modulators of RNA virus gene expression
Abstract
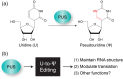
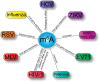
Epitranscriptomics, the study of posttranscriptional chemical moieties placed on RNA, has blossomed in recent years. This is due in part to the emergence of high-throughput detection methods as well as the burst of discoveries showing biological function of select chemical marks. RNA modifications have been shown to affect RNA structure, localization, and functions such as alternative splicing, stabilizing transcripts, nuclear export, cap-dependent and cap-independent translation, microRNA biogenesis and binding, RNA degradation, and immune regulation. As such, the deposition of chemical marks on RNA has the unique capability to spatially and temporally regulate gene expression. The goal of this article is to present the exciting convergence of the epitranscriptomic and virology fields, specifically the deposition and biological impact of N7-methylguanosine, ribose 2'-O-methylation, pseudouridine, inosine, N6-methyladenosine, and 5-methylcytosine epitranscriptomic marks on gene expression of RNA viruses. This article is categorized under: RNA in Disease and Development > RNA in Disease RNA Interactions with Proteins and Other Molecules > Protein-RNA Interactions: Functional Implications.
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine; N6-methyladenosine; N7-methylguanosine; RNA virus; epitranscriptomics; innate immunity; inosine; pseudouridine; ribose 2′-O-methylation.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures




References
-
- Abbas, Y. M. , Laudenbach, B. T. , Martínez‐Montero, S. , Cencic, R. , Habjan, M. , Pichlmair, A. , … Nagar, B. (2017). Structure of human IFIT1 with capped RNA reveals adaptable mRNA binding and mechanisms for sensing N1 and N2 ribose 2′‐O methylations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(11), E2106–E2115. 10.1073/pnas.1612444114 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson, B. R. , Muramatsu, H. , Jha, B. K. , Silverman, R. H. , Weissman, D. , & Karikó, K. (2011). Nucleoside modifications in RNA limit activation of 2′‐5′‐oligoadenylate synthetase and increase resistance to cleavage by RNase L. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(21), 9329–9338. 10.1093/nar/gkr586 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson, B. R. , Muramatsu, H. , Nallagatla, S. R. , Bevilacqua, P. C. , Sansing, L. H. , Weissman, D. , & Karikó, K. (2010). Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA enhances translation by diminishing PKR activation. Nucleic Acids Research, 38(17), 5884–5892. 10.1093/nar/gkq347 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

