Tip-apex distance and other predictors of outcome in cephalomedullary nailing of unstable trochanteric fractures
- PMID: 31695266
- PMCID: PMC6823765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2019.04.018
Tip-apex distance and other predictors of outcome in cephalomedullary nailing of unstable trochanteric fractures
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 Nov-Dec;11(6):1169-1171. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.09.032. Epub 2020 Sep 26. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 33013141 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum regarding missing Declaration of Competing Interest statements in previously published articles.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 Nov-Dec;11(6):1177. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.10.025. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 33078051 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 Nov-Dec;11(6):1172-1174. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.10.044. Epub 2020 Oct 23. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 33192025 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021 Aug 5;21:101557. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.101557. eCollection 2021 Oct. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021. PMID: 34414071 Free PMC article.
Abstract
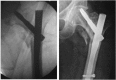
Background: Cephalomedullary nails are presently the gold standard in management of unstable trochanteric fractures. The tip-apex distance (TAD) is one of the most important factors that determines success or failure of fixation, but was described originally in context of an extramedullary hip screw. Cephalomedullary nails use a different biomechanical approach to fixation; and it is hypothesized that the TAD rule may not apply similarly with these. The aim of this study is to assess whether a high TAD correlates with poor outcomes with cephalomedullary nails, and to elucidate other factors that may predict such outcome.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the clinical and radiographic records of patients with intertrochanteric fractures, treated at our institution over a 2-year period. Those with unstable fractures (31.A2 and 31.A3), and who were treated with cephalomedullary nails were included in the study. The TAD and the position of the device in the femoral head (Cleveland index) were assessed. Other factors that could influence outcome like age, gender, AO fracture type, restoration of neck-shaft angle and degree of osteoporosis were analysed. Radiographic records of up-to at-least 3 months post-operatively were assessed for complications.
Results: After applying the exclusion criteria, 75 patients were included in the analysis. The overall rate of complications was 12%. They occurred in two major patterns - varus collapse and cut-out occurred in 5 patients (6.67%), and device migration in 4 patients (5.33%). The average TAD of patients with cut-out was 28.78 mm, compared to 19.44 mm in those without cut-out (p = 0.002). Our data predicted a cut-off TAD >23.56 mm as most significant for cut-out with cephalomedullary nails. On univariate logistic regression, high TAD (p = 0.009), sub-optimal device positioning (p = 0.02) and poor restoration of neck-shaft angle (p = 0.04) were found to be significant for varus collapse and cut-out, but not for complications relating to device migration. On multivariate analysis, none of the above factors reached statistical significance in isolation.
Conclusion: As with extramedullary devices, TAD, along with sub-optimal device positioning and poor restoration of neck-shaft angle is a useful predictor of cut-out even with cephalomedullary nails, negating the initial hypothesis. The above factors in combination have a more significant effect than any one factor in isolation to cause varus collapse and implant cut-out. However these do not affect Z effect, reverse Z effect or other types of device migration seen especially with dual-screw nails.
Keywords: Cephalomedullary nails; Cut-out; Implant failure; Intertrochanteric fractures; Tip-apex distance.
© 2019 Delhi Orthopedic Association. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Al-yassari G., Langstaff R.J., Jones J.W., Al-Lami M. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN) for the treatment of unstable trochanteric femoral fracture. Injury. 2002;33:395–399. - PubMed
-
- Schipper I.B., Bresina S., Wahl D., Linke B., Van Vugt A.B., Schneider E. Biomechanical evaluation of the proximal femoral nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002 Dec;(405):277–286. - PubMed
-
- Hohendorff B., Meyer P., Menezes D., Meier L., Elke R. Treatment results and complications after PFN osteosynthesis. Unfallchirurg. 2005;108(11) 938, 940, 941-46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous