Long non-coding RNA LINC00665 gastric cancer tumorigenesis by regulation miR-149-3p/RNF2 axis
- PMID: 31695413
- PMCID: PMC6717843
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S214588
Long non-coding RNA LINC00665 gastric cancer tumorigenesis by regulation miR-149-3p/RNF2 axis
Abstract
Background: Recently, LINC00665 has been reported to be a pivotal regulator in kinds of malignancy, such as lung cancer and liver cancer. However, the functions and underlying mechanisms of LINC00665 in gastric cancer (GC) remain unclear.
Materials and methods: We recruited 49 paired GC tissue to explore LINC00665 expression by qRT-PCR. In vitro function assays were used to explore the roles of LINC00665 in GC progression. Moreover, the interaction among LINC00665, miR-149-3p and RNF2 was explored by bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay.
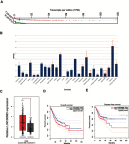
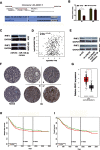
Results: In the present study, we found that LINC00665 expression was significantly elevated in GC tissues and cell lines. High LINC00665 expression was associated with TNM stage, histological grade, and poor prognosis of GC patients. Function assays showed that LINC00665 suppression significantly reduced GC cells viability and invasion ability in vitro. Mechanistic analysis showed that LINC00665 might serve as a ceRNA for miR-149-3p to regulate the expression of RNF2.
Conclusion: Our current study revealed the LINC00665/miR-149-3p/RNF2 axis was involved in GC progression, providing novel insights into the treatment for GC.
Keywords: LINC00665; RNF2; gastric cancer; miR-149-3p.
© 2019 Qi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Biological and Molecular Function of LINC00665 in Human Cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 May 19;12:886034. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.886034. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35664776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paeonol inhibits the malignancy of Apatinib-resistant gastric cancer cells via LINC00665/miR-665/MAPK1 axis.Phytomedicine. 2022 Feb;96:153903. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153903. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35026514
-
LINC00665 Promotes the Progression of Multiple Myeloma by Adsorbing miR-214-3p and Positively Regulating the Expression of PSMD10 and ASF1B.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 7;13:6511-6522. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S241627. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Jun 01;14:3535. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S321549. PMID: 32764956 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
LINC00665 Targets miR-214-3p/MAPK1 Axis to Accelerate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Warburg Effect.J Oncol. 2021 Nov 10;2021:9046798. doi: 10.1155/2021/9046798. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34804162 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00665: An Emerging Biomarker for Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics.Cells. 2022 May 4;11(9):1540. doi: 10.3390/cells11091540. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LINC00665 promotes the progression of acute myeloid leukemia by regulating the miR-4458/DOCK1 pathway.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 3;11(1):5009. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82834-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33658535 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological and Molecular Function of LINC00665 in Human Cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 May 19;12:886034. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.886034. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35664776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of LINC00665 inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via competitive binding of miR-3619-5p and inhibition of catenin beta 1.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020 Sep 24;25:43. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-00235-8. eCollection 2020. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32983239 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methyltransferase 3 beta regulates promoter methylation of microRNA-149 to augment esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development through the ring finger protein 2/Wnt/β-catenin axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):4010-4027. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2031411. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35129056 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-coding RNA LINC01503 Promotes Gastric Cardia Adenocarcinoma Progression via miR-133a-5p/VIM Axis and EMT Process.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Oct;66(10):3391-3403. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06690-9. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33200343
References
-
- Brenner H, Rothenbacher D, Arndt V. Epidemiology of Stomach cancer[M]//Cancer Epidemiology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2009:467–477. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

