Development and Use of the Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Review
- PMID: 31697310
- PMCID: PMC7859915
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3869
Development and Use of the Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Review
Abstract
Importance: Axicabtagene ciloleucel, an anti-CD19-CD28-CD3ζ chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, was the first US Food and Drug Administration-approved, genetically engineered T-cell therapy for adults with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) after 2 or more lines of systemic therapy. There has not been a US Food and Drug Administration-approved product for these cancers in more than 4 decades.
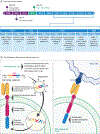
Observations: Unlike traditional anticancer therapies, axicabtagene ciloleucel is a patient-specific, live-cell product that has unique requirements for manufacturing, shipping, and storage, as well as for its administration and management of its adverse events. In addition, axicabtagene ciloleucel has demonstrated efficacy in patients with refractory LBCL. This review presents a timeline of the rapid clinical development of axicabtagene ciloleucel from bench to bedside, highlights how axicabtagene ciloleucel satisfies an unmet medical need for treatment of refractory LBCL, outlines the logistics of the production process and administration of axicabtagene ciloleucel, describes its mechanism of action, and summarizes the results of the pivotal study. This review also provides a survey of adverse events, with attention to the kinetics of their clinical presentation; discusses the management of adverse events; and offers suggestions for appropriate patient selection for safe administration of axicabtagene ciloleucel.
Conclusions and relevance: The integration of axicabtagene ciloleucel therapy into standard-of-care practice for relapsed/refractory LBCL is the beginning of a paradigm shift in the treatment of patients with LBCL and is likely to lead to improvements in their survival and curability. Timely referral to centers offering the therapy is necessary for optimal patient outcomes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Axicabtagene Ciloleucel: Clinical Data for the Use of CAR T-cell Therapy in Relapsed and Refractory Large B-cell Lymphoma.Ann Pharmacother. 2021 Mar;55(3):390-405. doi: 10.1177/1060028020944233. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Ann Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 32698673
-
Axicabtagene Ciloleucel, an Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Practical Implications for the Community Oncologist.Oncologist. 2020 Jan;25(1):e138-e146. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0395. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 31585984 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20(1):31-42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30864-7. Epub 2018 Dec 2. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30518502 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety evaluation of axicabtagene ciloleucel for relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2023 Jan;22(1):5-15. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2023.2177268. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2023. PMID: 36737060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EMA Review of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Yescarta) for the Treatment of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Oncologist. 2020 Oct;25(10):894-902. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0646. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32339368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CAR-T in Cancer Treatment: Develop in Self-Optimization, Win-Win in Cooperation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 19;13(8):1955. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081955. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pharmacovigilance Study on the Safety of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel Based on Spontaneous Reports from the EudraVigilance Database.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 1;11(8):2162. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082162. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626659 Free PMC article.
-
B-Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA) as a Target for New Drug Development in Relapsed and/or Refractory Multiple Myeloma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 22;21(15):5192. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155192. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32707894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Apr 25;51(2):167-174. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2022-0049. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36161292 Free PMC article. English.
-
[Mechanism and prevention strategies of neurotoxicity in CAR-T treatment of B cell tumors].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Sep 14;42(9):787-792. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2021.09.016. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34753239 Free PMC article. Chinese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cunningham D, Hawkes EA, Jack A, et al. Rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone in patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a phase 3 comparison of dose intensification with 14-day versus 21-day cycles. Lancet. 2013;381(9880):1817–1826. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60313-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilson WH, sin-Ho J, Pitcher BN, et al. Phase III randomized study of R-CHOP versus DA-EPOCH-R and molecular analysis of untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: CALGB/Alliance 50303. Blood. 2016;128(22):469.
-
- Gisselbrecht C, Schmitz N, Mounier N, et al. Rituximab maintenance therapy after autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with relapsed CD20+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: final analysis of the collaborative trial in relapsed aggressive lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2012;30(36):4462–4469. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.41.9416 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

