Microglia/Brain Macrophages as Central Drivers of Brain Tumor Pathobiology
- PMID: 31697921
- PMCID: PMC7288606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.08.028
Microglia/Brain Macrophages as Central Drivers of Brain Tumor Pathobiology
Abstract
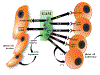
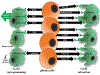
One of the most common brain tumors in children and adults is glioma or astrocytoma. There are few effective therapies for these cancers, and patients with malignant glioma fare poorly, even after aggressive surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Over the past decade, it is now appreciated that these tumors are composed of numerous distinct neoplastic and non-neoplastic cell populations, which could each influence overall tumor biology and response to therapy. Among these noncancerous cell types, monocytes (microglia and macrophages) predominate. In this Review, we discuss the complex interactions involving microglia and macrophages relevant to glioma formation, progression, and response to therapy.
Keywords: glioblastoma; glioma; immune; macrophages; microglia; monocyte.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
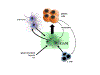
References
-
- a Dzaye OD, Hu F, Derkow K, Haage V, Euskirchen P, Harms C, Lehnardt S, Synowitz M, Wolf SA, and Kettenmann H (2016), Glioma Stem Cells but Not Bulk Glioma Cells Upregulate IL-6 Secretion in Microglia/Brain Macrophages via Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling, Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology, 75(5), 429–440, doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlw016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen AR, Eilertson K, Chakraborti A, Sharma S, Baure J, Habdank-Kolaczkowski J, Allen B, Rosi S, Raber J, and Fike JR (2014), Radiation exposure prior to traumatic brain injury induces responses that differ as a function of animal age, Int J Radiat Biol, 90(3), 214–223, doi: 10.3109/09553002.2014.859761. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badie B, and Schartner JM (2000), Flow cytometric characterization of tumor-associated macrophages in experimental gliomas, Neurosurgery, 46(4), 957–961; discussion 961–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

