Burden of headache disorders in China, 1990-2017: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
- PMID: 31699022
- PMCID: PMC6836347
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-019-1048-2
Burden of headache disorders in China, 1990-2017: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
Abstract
Background: Headache has emerged as a global public health concern. However, little is known about the burden from headache disorders in China. The aim of this work was to quantify the spatial patterns and temporal trends of burden from headache disorders in China.
Methods: Following the general analytic strategy used in the 2017 Global Burden of Disease study, we analyzed the prevalence and years lived with disability (YLDs) of headache and its main subcategories, including migraine and tension-type headache (TTH), by age, sex, year and 33 province-level administrative units in China from 1990 to 2017.
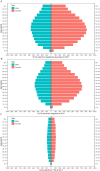
Results: Almost 112.4 million individuals were estimated to have headache disorders in 1990 in China, which rose to 482.7 million in 2017. The all-age YLDs increased by 36.2% from 1990 to 2017. Migraine caused 5.5 million YLDs, much higher than TTH (1.1 million) in 2017. The age-standardized prevalence and YLDs rate of headache remained stable and high in 2017 compared with 1990, respectively. The proportion of total headache YLDs in all diseases increased from 1990 to 2017 by 5.4%. A female preponderance was observed for YLDs and the YLDs were mainly in people aged 20~54 years.
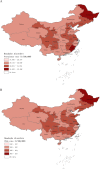
Conclusions: Headache remains a huge health burden in China from 1990 to 2017, with prevalence and YLDs rates higher in eastern provinces than western provinces. The substantial increase in headache cases and YLDs represents an ongoing challenge in Chinese population. Our results can help shape and inform headache research and public policy throughout China, especially for females and middle-aged people.
Keywords: China; Global Burden of Disease Study; Headache disorders; Migraine; Prevalence; Tension-type headache; Years lived with disability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

