Can infections trigger alpha-synucleinopathies?
- PMID: 31699323
- PMCID: PMC6857718
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2019.06.002
Can infections trigger alpha-synucleinopathies?
Abstract
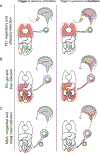
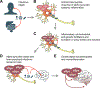
As synucleinopathies, Parkinson's disease (PD) and multiple system atrophy (MSA) are neurodegenerative diseases that involve the spread of pathogenic alpha-synuclein (αSyn) throughout the brain. Recent studies have suggested a role for αSyn as an antimicrobial peptide in response to PD- and MSA-related infections of peripheral tissues, including those in the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and urogenital systems. In this chapter, we examine epidemiological and experimental evidence for a role of peripheral microbial infections in triggering alpha-synucleinopathies. We propose a model of how infectious triggers, in conjunction with inflammatory, environmental, and genetic facilitators, may result in transfer of pathogenic αSyn strains from the periphery to the brain, where they propagate and spread. Finally, we discuss future research challenges and programs necessary to clarify the role of infections as triggers of PD and MSA and, ultimately, to prevent the onset of these diseases by infectious triggers.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Antimicrobial peptides; Bacteria; Facilitators; Fungi; Infections; Multiple system atrophy; Parkinson's disease; Triggers; Viruses.
© 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no additional competing financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

