Quantitating the epigenetic transformation contributing to cholesterol homeostasis using Gaussian process
- PMID: 31699992
- PMCID: PMC6838179
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12969-x
Quantitating the epigenetic transformation contributing to cholesterol homeostasis using Gaussian process
Abstract
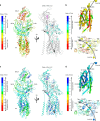
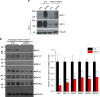
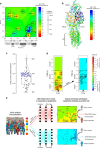
To understand the impact of epigenetics on human misfolding disease, we apply Gaussian-process regression (GPR) based machine learning (ML) (GPR-ML) through variation spatial profiling (VSP). VSP generates population-based matrices describing the spatial covariance (SCV) relationships that link genetic diversity to fitness of the individual in response to histone deacetylases inhibitors (HDACi). Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) is a Mendelian disorder caused by >300 variants in the NPC1 gene that disrupt cholesterol homeostasis leading to the rapid onset and progression of neurodegenerative disease. We determine the sequence-to-function-to-structure relationships of the NPC1 polypeptide fold required for membrane trafficking and generation of a tunnel that mediates cholesterol flux in late endosomal/lysosomal (LE/Ly) compartments. HDACi treatment reveals unanticipated epigenomic plasticity in SCV relationships that restore NPC1 functionality. GPR-ML based matrices capture the epigenetic processes impacting information flow through central dogma, providing a framework for quantifying the effect of the environment on the healthspan of the individual.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. The authors declare no advisory, management, or consulting positions. C.W. and W.E.B. have filed PCT Application Serial No. PCT/US2019/046028.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantitative Analysis of the Proteome Response to the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor (HDACi) Vorinostat in Niemann-Pick Type C1 disease.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Nov;16(11):1938-1957. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.064949. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28860124 Free PMC article.
-
Individualized management of genetic diversity in Niemann-Pick C1 through modulation of the Hsp70 chaperone system.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Jan 1;29(1):1-19. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz215. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 31509197 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors correct the cholesterol storage defect in most Niemann-Pick C1 mutant cells.J Lipid Res. 2017 Apr;58(4):695-708. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M072140. Epub 2017 Feb 13. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28193631 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Niemann--pick type C disease by histone deacetylase inhibitors.Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Oct;10(4):688-97. doi: 10.1007/s13311-013-0217-2. Neurotherapeutics. 2013. PMID: 24048860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment trials in Niemann-Pick type C disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Dec;36(8):2215-2221. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00842-0. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 34596813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Species-specific differences in NPC1 protein trafficking govern therapeutic response in Niemann-Pick type C disease.JCI Insight. 2022 Dec 8;7(23):e160308. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.160308. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 36301667 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the host-pathogen evolutionary balance through Gaussian process modeling of SARS-CoV-2.Patterns (N Y). 2023 Jul 21;4(8):100800. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100800. eCollection 2023 Aug 11. Patterns (N Y). 2023. PMID: 37602209 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Bromodomain Proteins as Drug Targets for Niemann-Pick Type C Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 16;26(12):5769. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125769. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565243 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Population Genomics for Individualized Correction of the Hallmarks of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency.Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2020 Jul;7(3):224-246. doi: 10.15326/jcopdf.7.3.2019.0167. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2020. PMID: 32726074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol Transport in Wild-Type NPC1 and P691S: Molecular Dynamics Simulations Reveal Changes in Dynamical Behavior.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 22;21(8):2962. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082962. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32331453 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

