Rapid and multi-cycle smFISH enabled by microfluidic ion concentration polarization for in-situ profiling of tissue-specific gene expression in whole C. elegans
- PMID: 31700560
- PMCID: PMC6824911
- DOI: 10.1063/1.5124827
Rapid and multi-cycle smFISH enabled by microfluidic ion concentration polarization for in-situ profiling of tissue-specific gene expression in whole C. elegans
Abstract
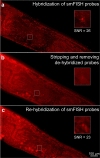
Understanding gene regulation networks in multicellular organisms is crucial to decipher many complex physiological processes ranging from development to aging. One technique to characterize gene expression with tissue-specificity in whole organisms is single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization (smFISH). However, this protocol requires lengthy incubation times, and it is challenging to achieve multiplexed smFISH in a whole organism. Multiplexing techniques can yield transcriptome-level information, but they require sequential probing of different genes. The inefficient macromolecule exchange through diffusion-dominant transport across dense tissues is the major bottleneck. In this work, we address this challenge by developing a microfluidic/electrokinetic hybrid platform to enable multicycle smFISH in an intact model organism, Caenorhabditis elegans. We integrate an ion concentration polarization based ion pump with a microfluidic array to rapidly deliver and remove gene-specific probes and stripping reagents on demand in individual animals. Using our platform, we can achieve rapid smFISH, an order of magnitude faster than traditional smFISH protocols. We also demonstrate the capability to perform multicycle smFISH on the same individual samples, which is impossible to do off-chip. Our method hence provides a powerful tool to study individual-specific, spatially resolvable, and large-scale gene expression in whole organisms.
Copyright © 2019 Author(s).
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
