Clinical management of autoimmune hepatitis
- PMID: 31700628
- PMCID: PMC6826525
- DOI: 10.1177/2050640619872408
Clinical management of autoimmune hepatitis
Abstract
Autoimmune hepatitis is a rare and chronic liver disease that is characterised by increased serum transaminases and immunoglobulin G, inflammatory liver histology and presence of circulating autoantibodies. An autoimmune hepatitis diagnosis justifies life-long treatment in most patients in order to prevent development of cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease. The cornerstone of treatment is steroid induction therapy followed by maintenance therapy with azathioprine, which is effective in most cases. For patients who do not respond to standard treatment, second-line treatment with other immunosuppressants can be effective. Treatment should be aimed at biochemical remission of the disease, which is defined as normalization of transaminases and immunoglobulin G. Patients should be monitored intensively during the first months of treatment in order to monitor side-effects, assess symptoms and individualise treatment. Specialist consultation should be sought in difficult-to-treat patients. Future studies and networking initiatives should result in optimization of current treatment strategies in autoimmune hepatitis.
Keywords: Autoimmune hepatitis; European Association for Study of the Liver; clinical management; induction therapy; prednisolone; prednisone.
© Author(s) 2019.
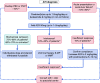
Figures
References
-
- Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D, Czaja AJ, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018; 4: 18017. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: Review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol 1999; 31: 929–938. - PubMed
-
- Soloway RD, Summerskill WH, Baggenstoss AH, et al. Clinical, biochemical, and histological remission of severe chronic active liver disease: A controlled study of treatments and early prognosis. Gastroenterology 1972; 63: 820–833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

