BioModels-15 years of sharing computational models in life science
- PMID: 31701150
- PMCID: PMC7145643
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz1055
BioModels-15 years of sharing computational models in life science
Abstract
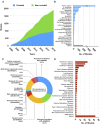
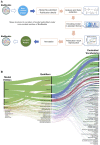
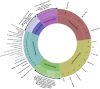
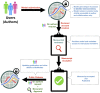
Computational modelling has become increasingly common in life science research. To provide a platform to support universal sharing, easy accessibility and model reproducibility, BioModels (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/biomodels/), a repository for mathematical models, was established in 2005. The current BioModels platform allows submission of models encoded in diverse modelling formats, including SBML, CellML, PharmML, COMBINE archive, MATLAB, Mathematica, R, Python or C++. The models submitted to BioModels are curated to verify the computational representation of the biological process and the reproducibility of the simulation results in the reference publication. The curation also involves encoding models in standard formats and annotation with controlled vocabularies following MIRIAM (minimal information required in the annotation of biochemical models) guidelines. BioModels now accepts large-scale submission of auto-generated computational models. With gradual growth in content over 15 years, BioModels currently hosts about 2000 models from the published literature. With about 800 curated models, BioModels has become the world's largest repository of curated models and emerged as the third most used data resource after PubMed and Google Scholar among the scientists who use modelling in their research. Thus, BioModels benefits modellers by providing access to reliable and semantically enriched curated models in standard formats that are easy to share, reproduce and reuse.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Le Novère N., Bornstein B., Broicher A., Courtot M., Donizelli M., Dharuri H., Li L., Sauro H., Schilstra M., Shapiro B. et al. .. BioModels Database: a free, centralized database of curated, published, quantitative kinetic models of biochemical and cellular systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006; 34:D689–D691. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- BB/J019305/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/P013414/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L502224/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J004456/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/P013406/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

