Caucasian Gentiana Species: Untargeted LC-MS Metabolic Profiling, Antioxidant and Digestive Enzyme Inhibiting Activity of Six Plants
- PMID: 31703419
- PMCID: PMC6918269
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo9110271
Caucasian Gentiana Species: Untargeted LC-MS Metabolic Profiling, Antioxidant and Digestive Enzyme Inhibiting Activity of Six Plants
Abstract
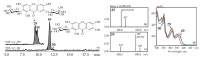
The members of Gentiana genus are widely distributed in the Caucasus region where they are used as phytoremedies, but they still have not been studied for their chemical composition and bioactivity. High-performance liquid chromatography with diode array and electrospray triple quadrupole mass detection (HPLC-DAD-ESI-QQQ-MS) was used to investigate metabolites of herb and roots of six gentians (Gentiana asclepiadea, G. cruciata, G. gelida, G. paradoxa, G. pneumonanthe, G. septemfida) grown in the Caucasus. In total, 137 compounds were found including three carbohydrates, 71 iridoid glycosides (mostly loganic acid), loganin, swertiamarin, gentiopicroside and sweroside derivatives, 40 flavones C-, O-, C,O-glycosides (such as luteolin, apigenin, chrysoeriol, and acacetin derivatives), two phenolic O-glycosides, five hydroxycinnamates, eight xanthones, and seven triterpene glycosides. Most of these compounds were identified in gentian samples for the first time. Quantitative differences were found in levels of seven iridoid glycosides, nine glycosylflavones, and two xanthones obtained by HPLC-DAD assay. The gentian extracts were evaluated for their radical-scavenging properties against DPPH and superoxide anion radicals, lipid peroxidation inhibition, and α-amylase/α-glycosidase inhibition. The herb extracts showed higher activity than root extracts. Positive correlations were found between the content of quantified phenolics and antioxidant and digestive enzymes inhibiting activity. The findings presented in our work suggest that the Caucasian gentians are a good source of bioactive phytocompounds with antioxidant and antidiabetic potential.
Keywords: Gentiana; LC-MS profile; amylase/glycosidase inhibition; antioxidant activity; flavone glycosides; iridoid glycosides; xanthones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









References
-
- The Plant List. [(accessed on 24 September 2019)]; Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/1.1/browse/A/Gentianaceae/Gentiana/
-
- Sirotuk E.A. Ph.D. Thesis. Kuban State Agrarian University; Krasnodar, Russia: Mar 22, 2007. The Gentians of the West Caucasus: The aspects of biology and conservation.
-
- Mamedov N., Mehdiyeva N.P., Craker L.E. Medicinal plants used in traditional medicine of the Caucasus and North America. J. Med. Act. Plants. 2015;4:42–66. doi: 10.7275/R51834DS. - DOI
-
- Ibadullayeva S.J., Mamedova S.E., Sultanova Z.R., Movsumova N.V., Jafarli I.A. Medicinal plants of Azerbaijan flora used in the treatment of certain diseases. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010;4:545–548.
-
- Karyagin I.I. Flora of Azerbaijan. Volume 7. Academy of Science; Baku, Azerbaijan: 1957. pp. 87–99.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

